Echoes Of An Ancient Burial
Strange clues etched into ancient stone keep reshaping how archaeologists view Jesus’ tomb. Each new find challenges long-held assumptions and hints at what may have unfolded inside one of history’s most debated burial sites.

The Tomb Of Jesus
The Tomb of Jesus is the burial place described in the Gospels, traditionally identified within Jerusalem’s Church of the Holy Sepulchre. It stands as a defining landmark in Christian tradition, linking scripture with historical presence.
 Anton Croos, Wikimedia Commons
Anton Croos, Wikimedia Commons
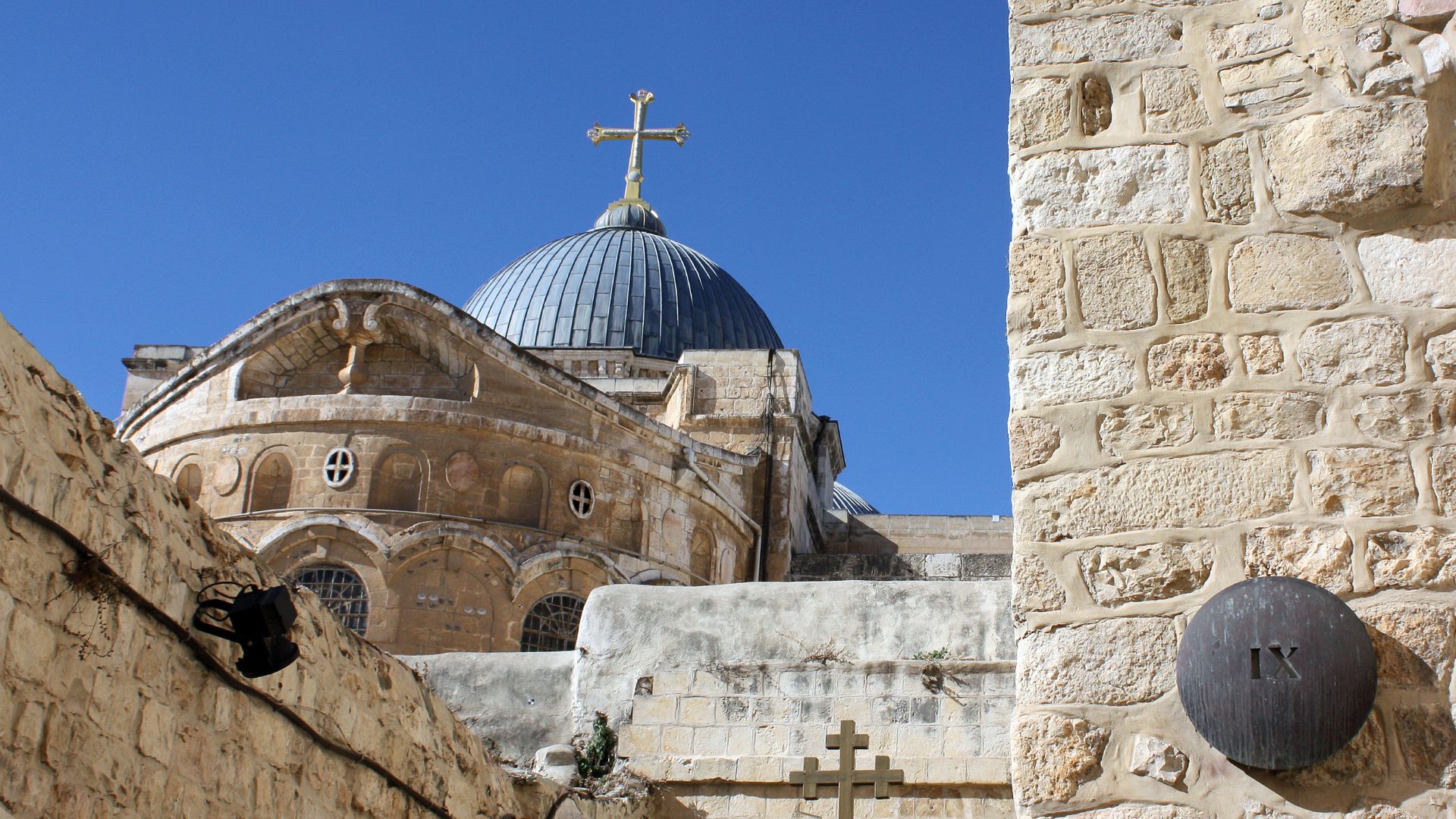
A Center Of Pilgrimage
The site anchors Christian belief in Jesus’s death, burial, and resurrection. It remains a central destination for pilgrimage and historical inquiry, and draws visitors worldwide who seek to connect faith with the enduring memory of sacred history.
Joseph Of Arimathea's Role
Joseph of Arimathea, a council member, offered his unused rock-cut burial chamber for Jesus's body. This act gave the Gospel account tangible detail. It connected scripture with a specific individual and his decisive gesture of generosity.
A Historical Anchor
The tomb linked to Joseph provides a historical anchor for understanding where Jesus's burial likely occurred. The site situates the Gospel narrative within a recognizable first-century context. Scholars and believers gain a clearer frame for interpreting sacred history through such geographical specificity.
Why Christians Honor The Holy Sepulchre
Because the Gospels describe a specific rock‑cut tomb offered for Jesus’s burial, Christian memory naturally gathers around the place believed to hold it, shaping devotion and anchoring faith in a tangible site of sacred history.
 Gary Todd from Xinzheng, China, Wikimedia Commons
Gary Todd from Xinzheng, China, Wikimedia Commons
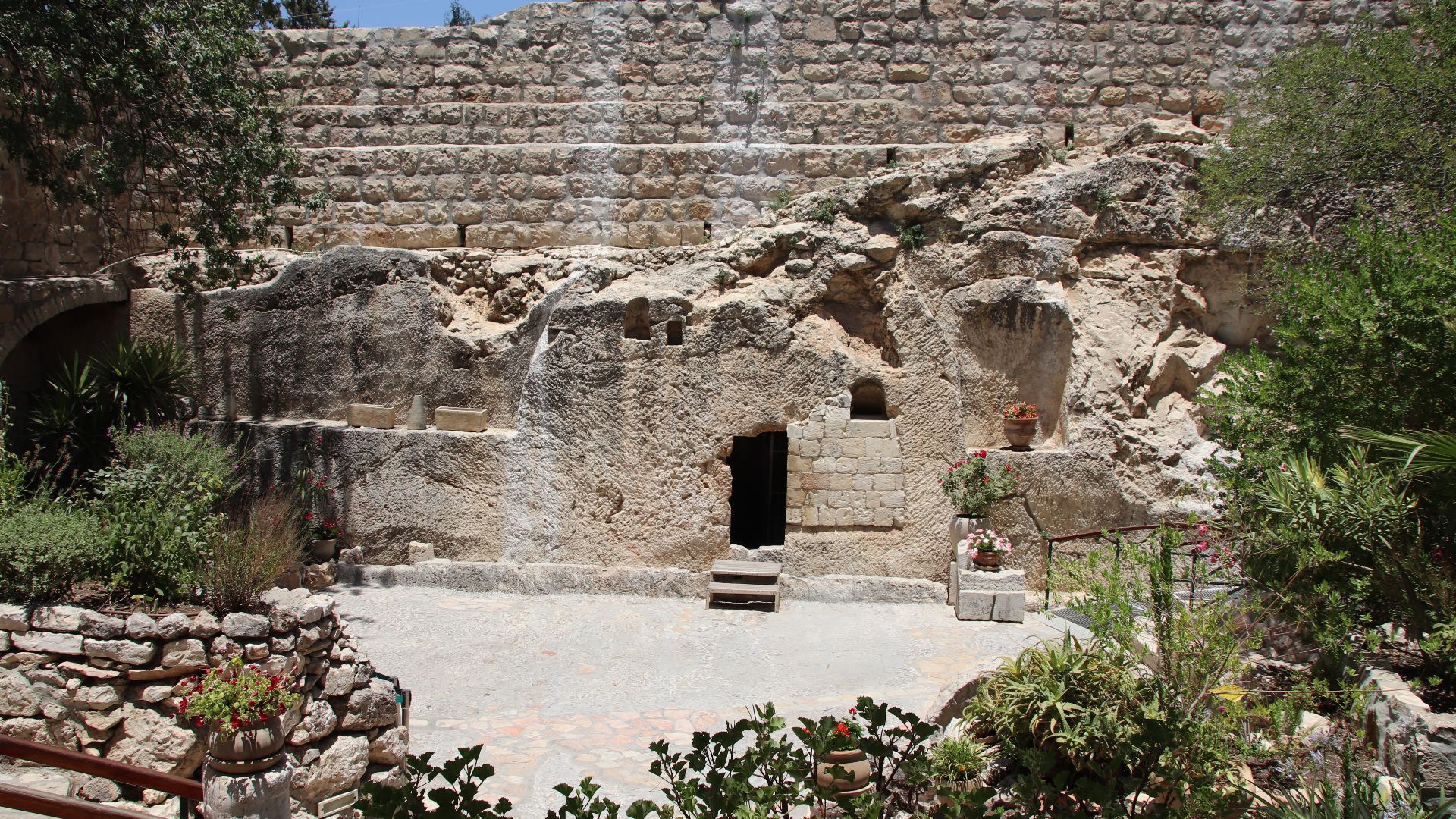
Why Christians Honor The Holy Sepulchre (Cont.)
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre is revered for enclosing both Golgotha and the tomb. This sacred complex unites Christianity’s defining moments into one focal point for pilgrimage and enduring religious significance.
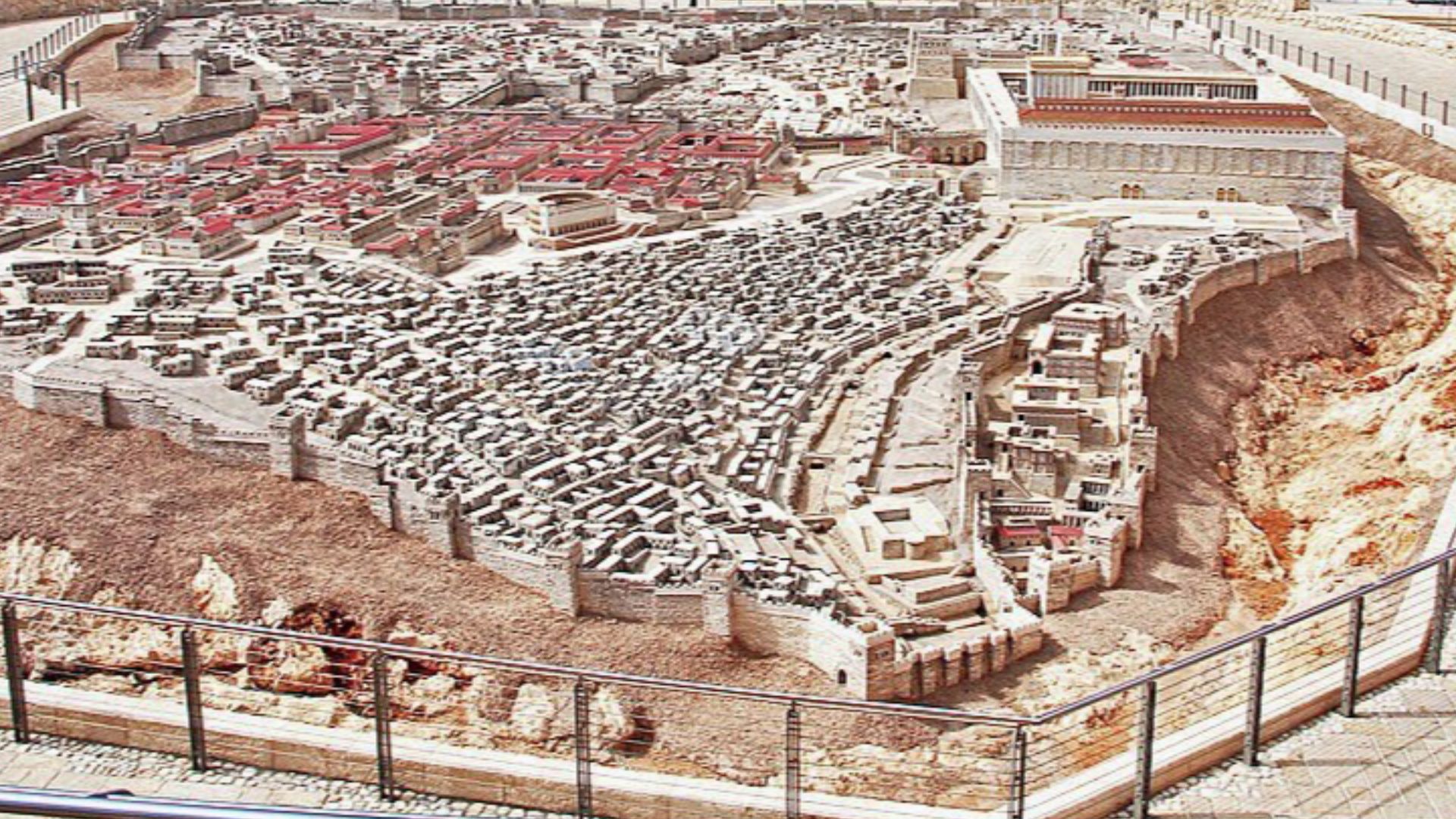
A Quarry That Matches The Gospel Setting
The church sits on a former stone quarry that lay outside Jerusalem’s walls during Jesus’s lifetime. That setting aligns with Gospel descriptions of an external crucifixion and burial area. It also strengthens the case for a first-century tomb surviving beneath the later structures built above it.
 Michael Tyler, Wikimedia Commons
Michael Tyler, Wikimedia Commons
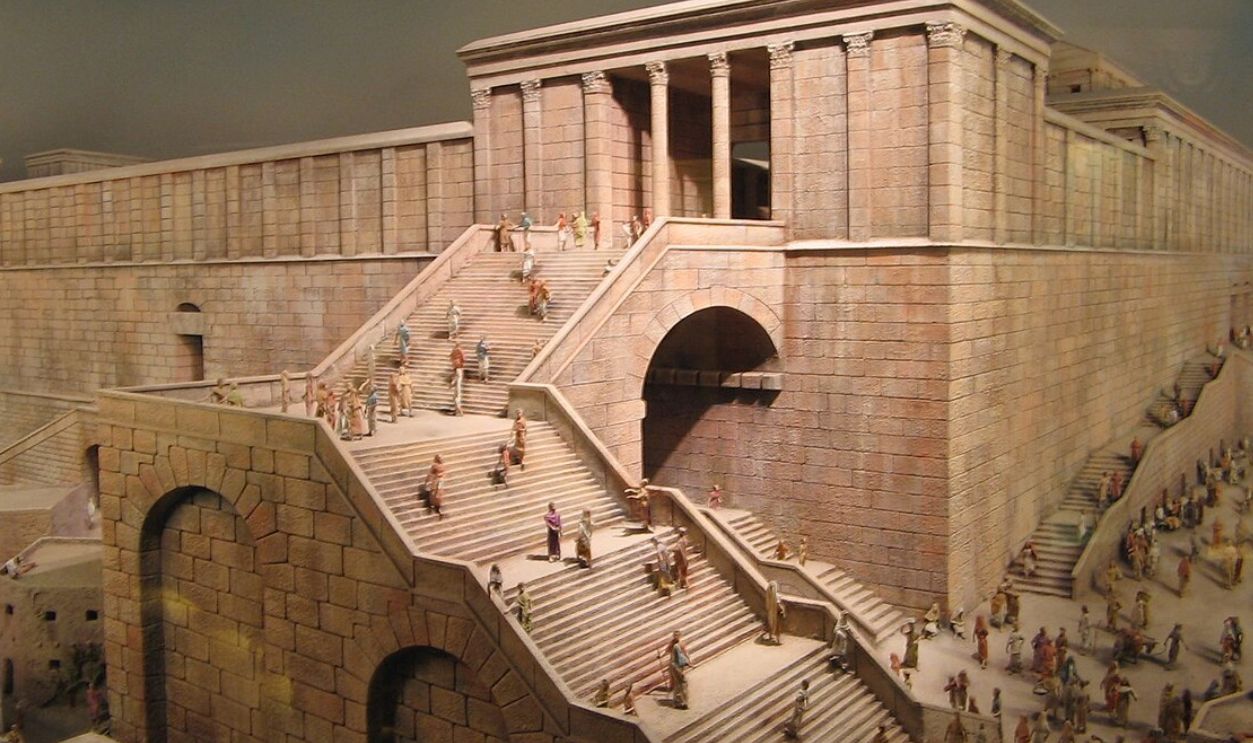
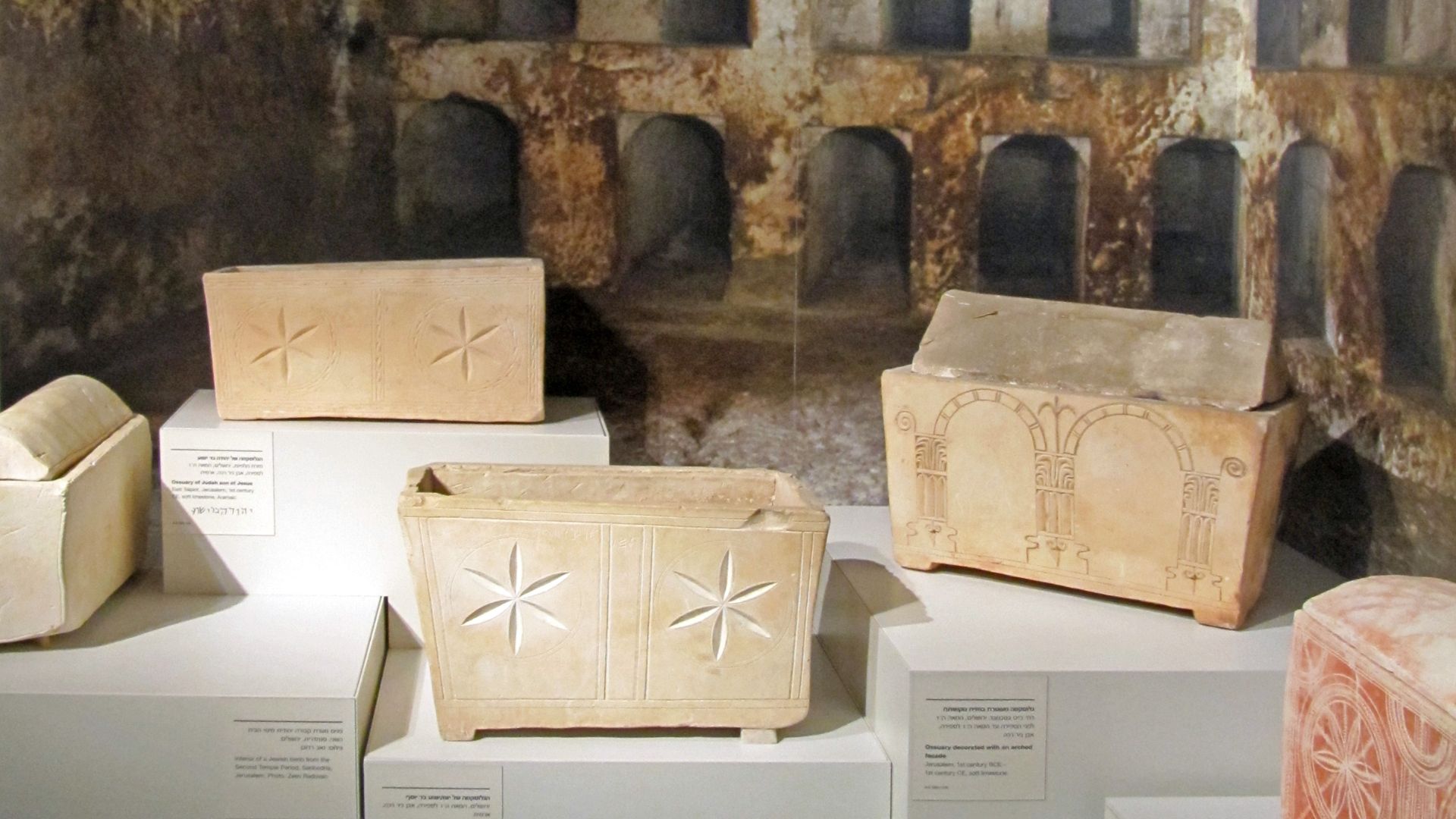
How First-Century Jews Buried Their Dead
Jewish customs called for washing a body, wrapping it in linen, and placing it on a stone bench, with bones later stored in ossuaries. Knowing this helps you see how the Gospel’s burial details—and its empty-tomb account—fit recognizable first-century practices.
 Jorge Royan, Wikimedia Commons
Jorge Royan, Wikimedia Commons

History's most fascinating stories and darkest secrets, delivered to your inbox daily.
Why Early Burials Occurred Outside City Walls
These customs also required burials outside city walls. Conrad Schick’s nineteenth-century surveys mapped the limits of Jerusalem’s Second Wall and showed the Holy Sepulchre lay beyond it in the first century. Set against the Gospel accounts, that layout strengthens the site’s credibility as a plausible burial location.
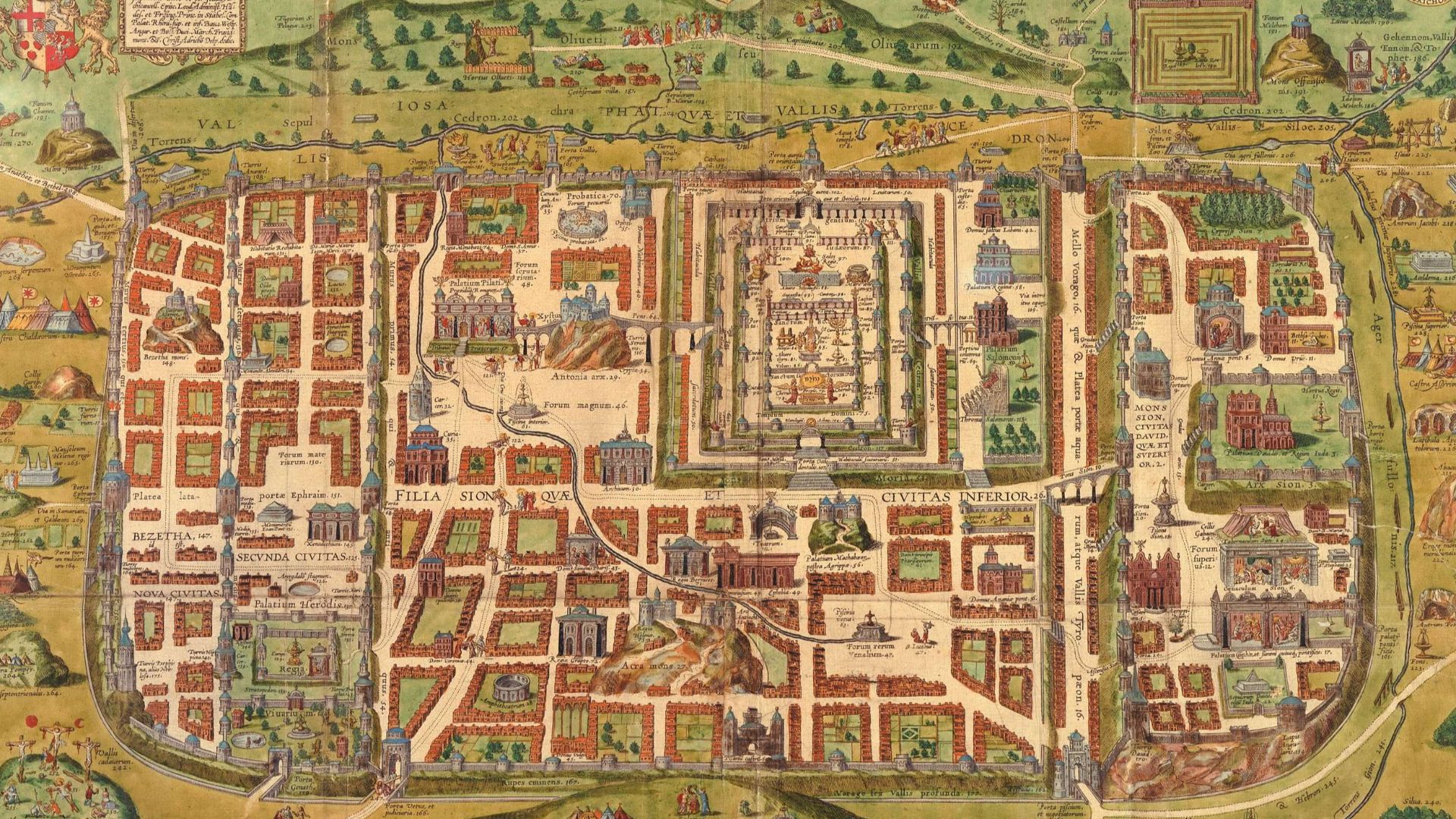
How Jerusalem’s Expanding Walls Hid The Tomb
As centuries passed, Jerusalem’s walls grew outward and eventually enclosed the tomb site. Recognizing those changes clarifies early Christian claims that it once lay outside the city and helps researchers bridge archaeological reconstructions with textual traditions composed well after Jesus’s lifetime.
 Christian Kruik van Adrichem (1533—1585)), Wikimedia Commons
Christian Kruik van Adrichem (1533—1585)), Wikimedia Commons
Why Early Christian Memory Still Carries Weight
Since the city’s boundaries shifted and eventually hid the original landscape, early Christian memory became even more important. Believers marked the Holy Sepulchre’s location long before those urban changes. That continuity strengthens its claim in ways alternative proposals like the Garden Tomb, Talpiot, Roza Bal, or Shingo cannot match.
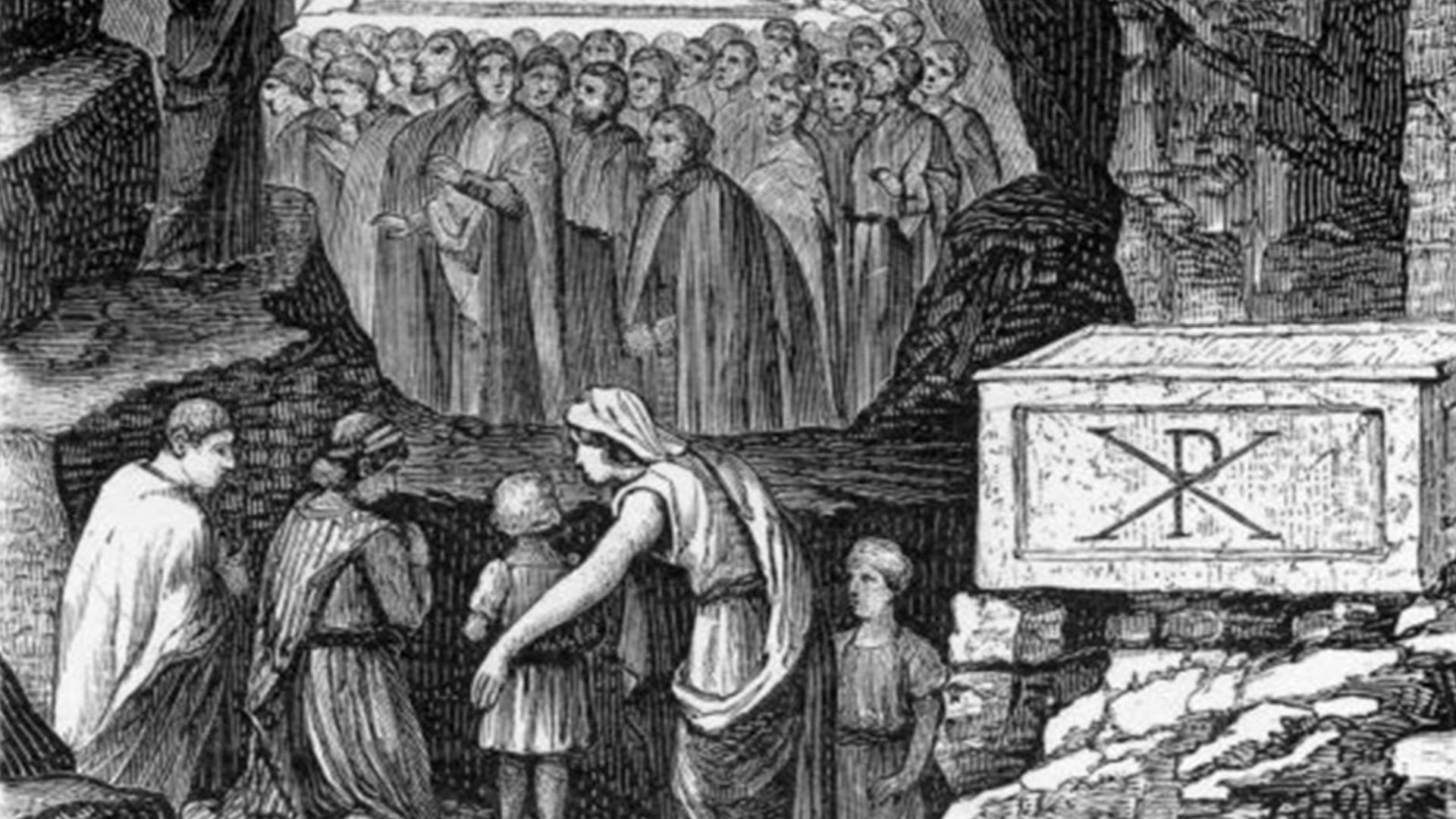 AnonymousUnknown author, Wikimedia Commons
AnonymousUnknown author, Wikimedia Commons
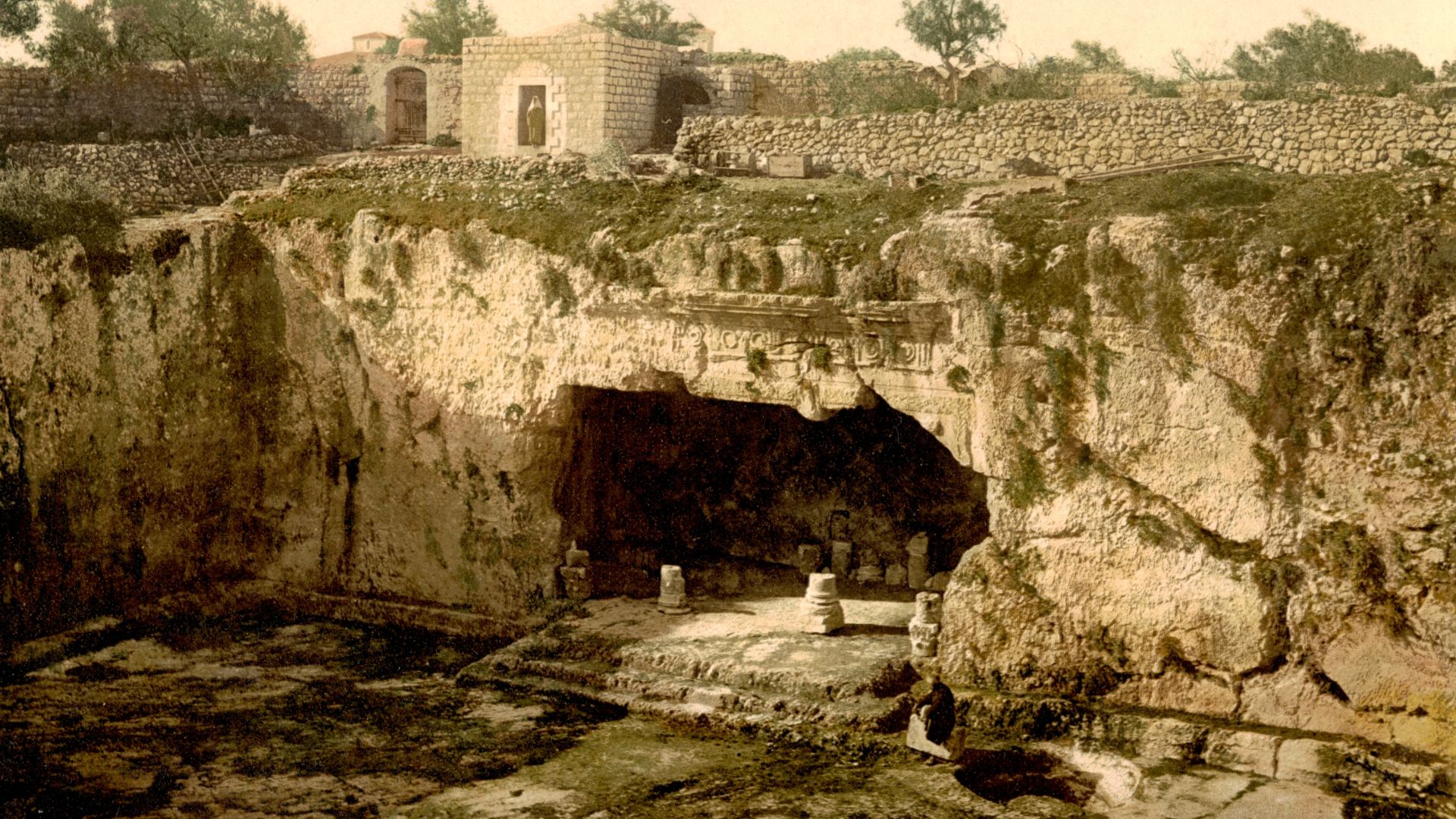
Helena’s Search For Jesus’s Tomb
Helena of Constantinople, mother of Emperor Constantine, traveled to Jerusalem in 326 CE. She identified a tomb beneath a Roman temple, a discovery that aligned with Christian tradition and guided Constantine’s building program, weaving faith into imperial authority.
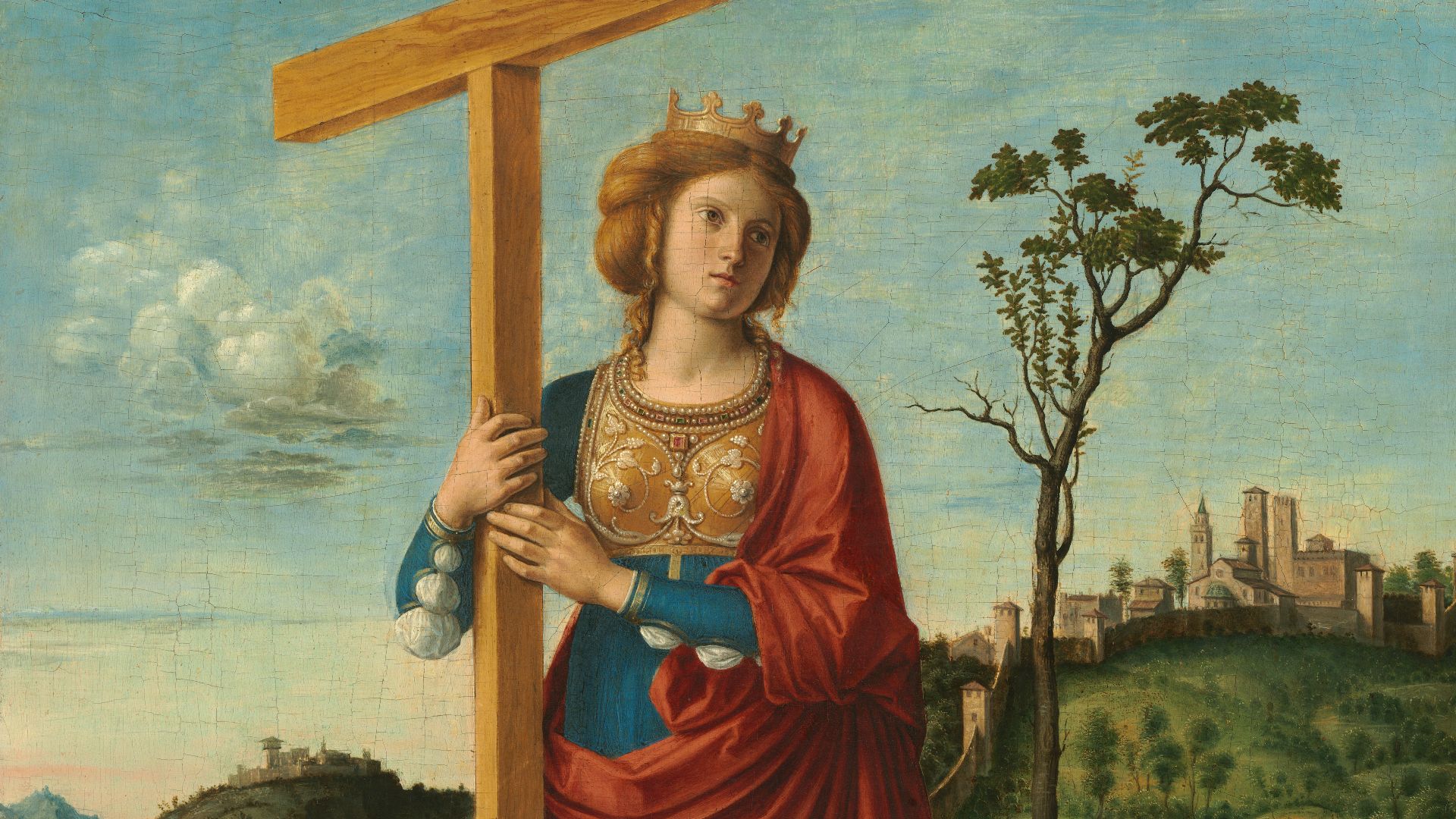 Giovanni Battista Cima da Conegliano, Wikimedia Commons
Giovanni Battista Cima da Conegliano, Wikimedia Commons
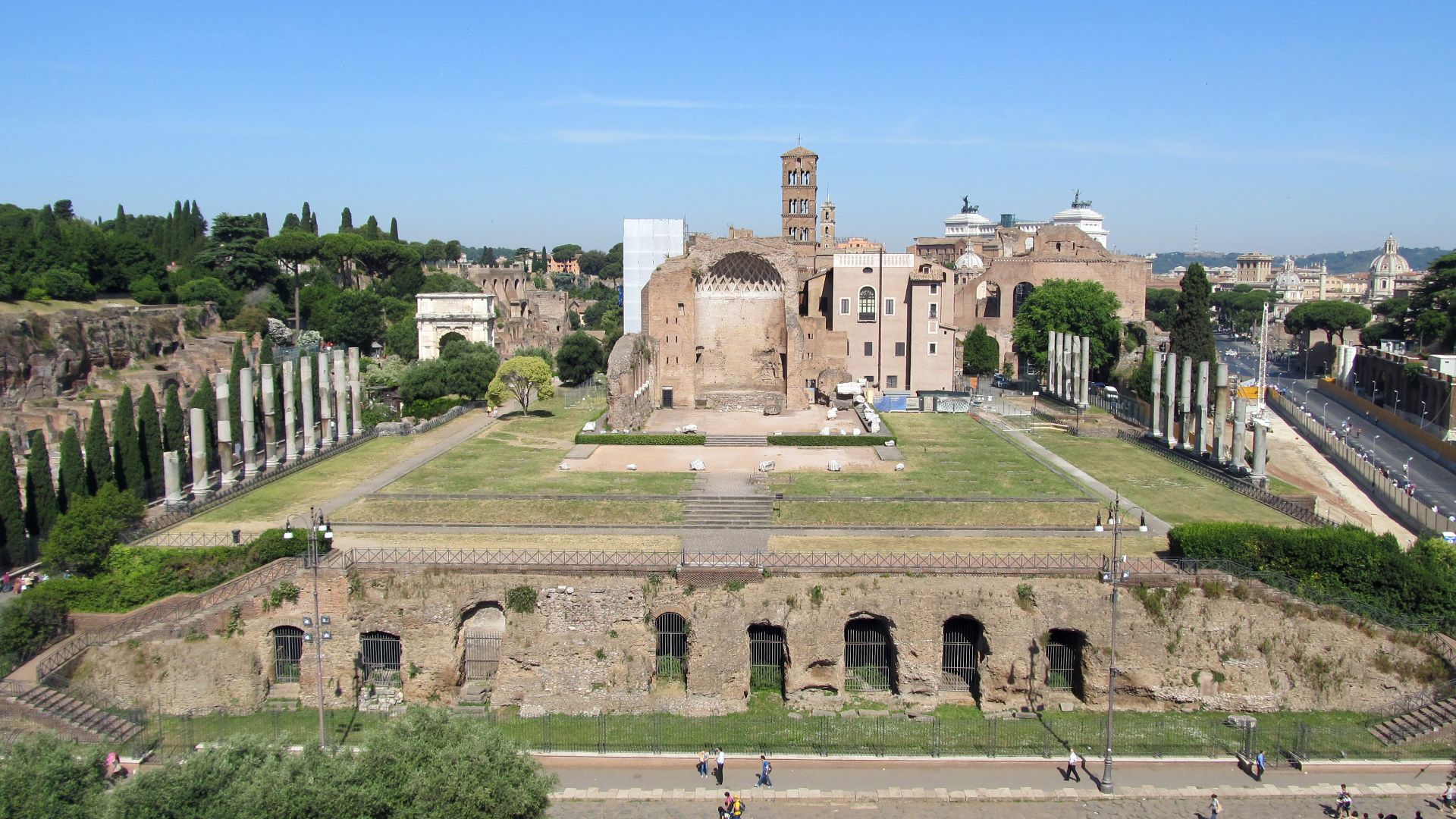
A Roman Temple That Accidentally Preserved The Site
Helena’s report focused attention on a location long occupied by Hadrian’s temple to Venus. Early Christians saw the temple as a deliberate overwrite of their sacred place, yet it ended up protecting the ground beneath it. This unintended preservation enabled Constantine’s builders to expose the buried area during excavation.
 daryl_mitchell from Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada, Wikimedia Commons
daryl_mitchell from Saskatoon, Saskatchewan, Canada, Wikimedia Commons
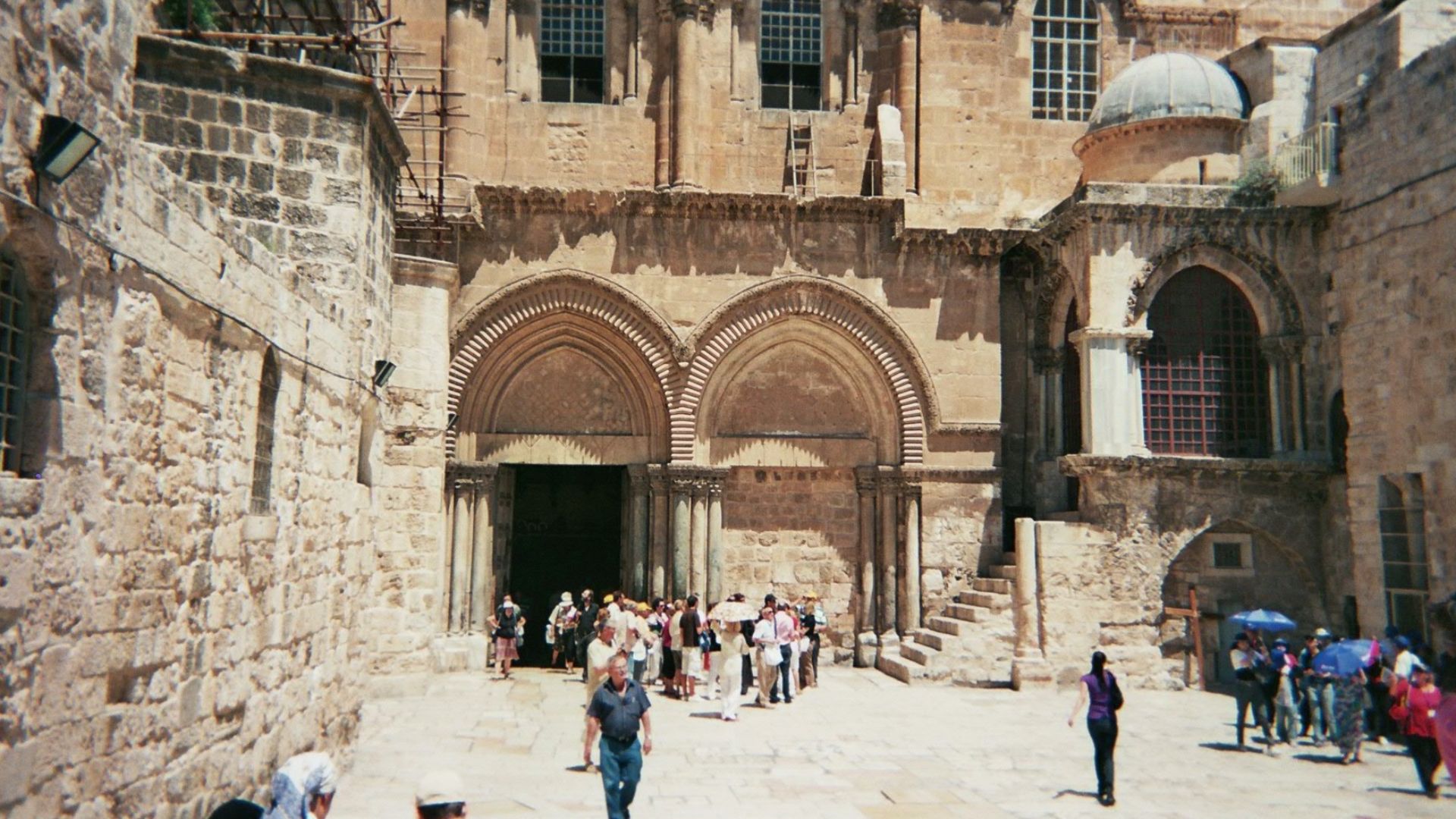
Constantine’s Excavation And Discovery
As Hadrian’s temple came down, workers uncovered a rock-cut tomb resembling the Gospel description. Constantine responded by creating the Holy Sepulchre complex, the earliest major church marking Jesus’s burial and resurrection, a project that guided Christian pilgrimage patterns long after you leave the narrative behind.
 fr:Utilisater:Djampa, Wikimedia Commons
fr:Utilisater:Djampa, Wikimedia Commons
What Early Pilgrims Saw And Recorded
Once Constantine’s builders revealed and enshrined the tomb, visitors began describing what they encountered there. The fourth-century pilgrim Egeria left some of the clearest accounts. Her observations of rituals and architecture give historians rare insight into how Christians understood and used the site soon after the complex took shape.
 Dennis G. Jarvis, Wikimedia Commons
Dennis G. Jarvis, Wikimedia Commons
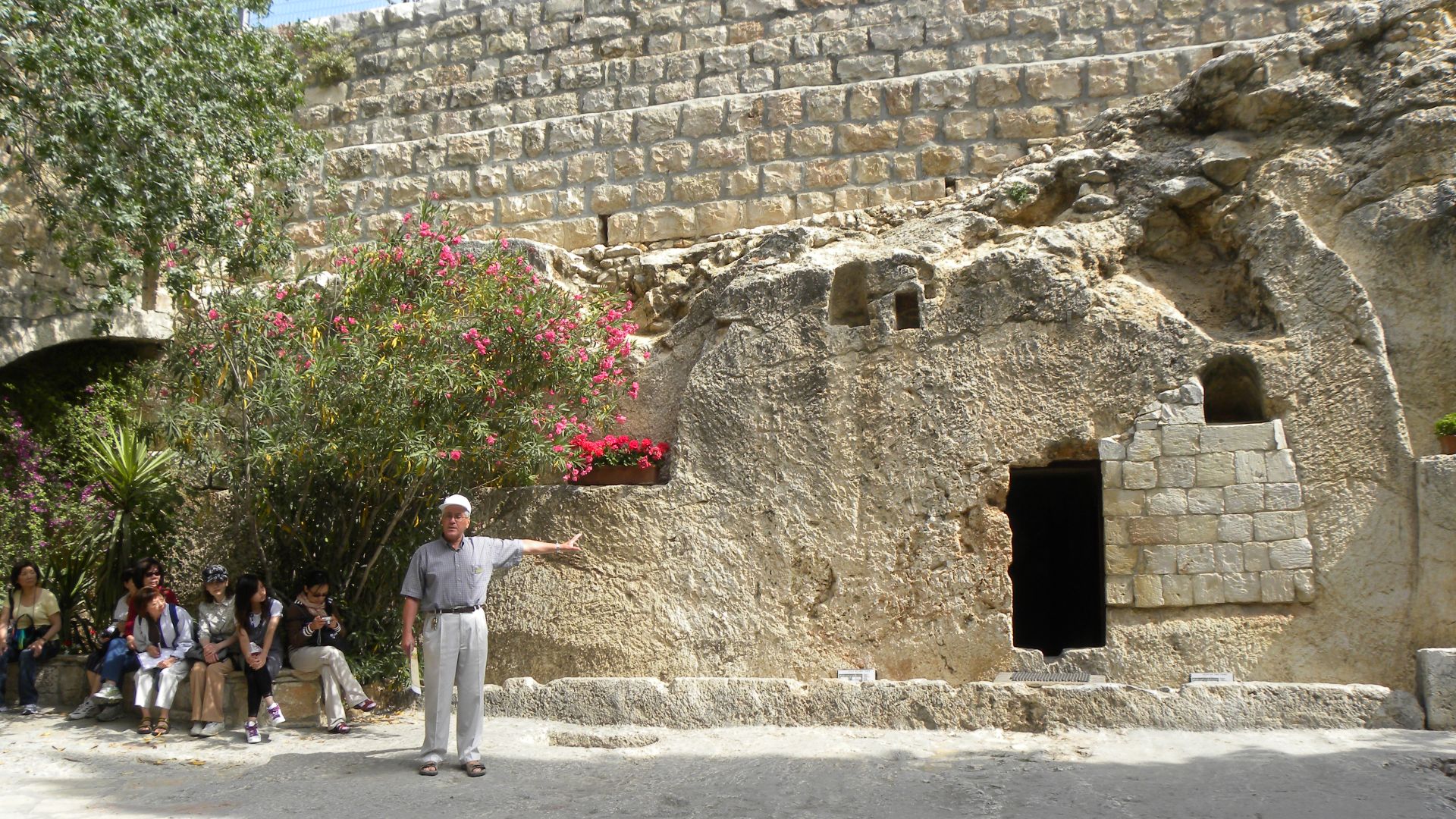
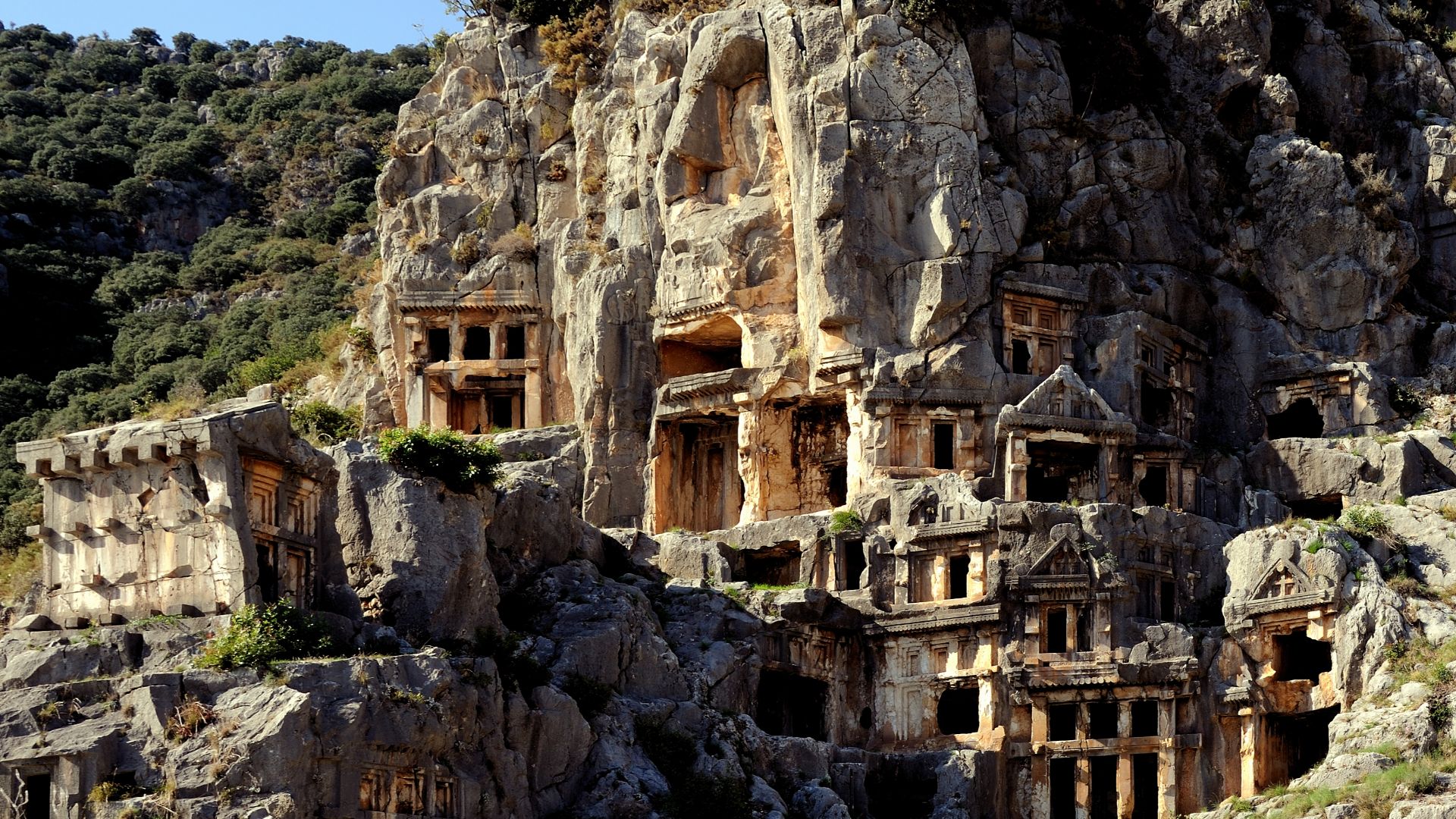
A Rock-Cut Tomb Consistent With The Gospels
Those early descriptions sit alongside the archaeological profile of the tomb itself. First-century Jerusalem burials relied on limestone chambers with benches or niches for the dead, a pattern mirrored in the Holy Sepulchre’s layout. The correspondence strengthens arguments for authenticity and matches the practices described in the New Testament.
 Saffron Blaze, Wikimedia Commons
Saffron Blaze, Wikimedia Commons
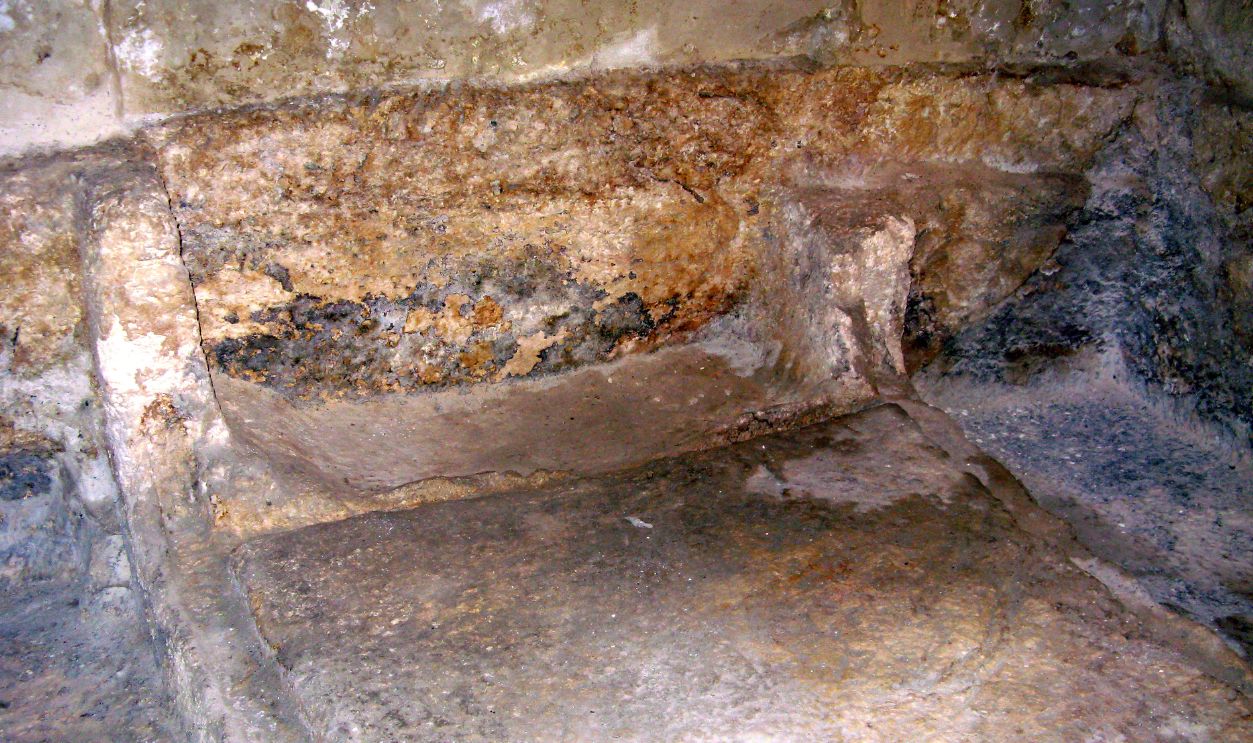
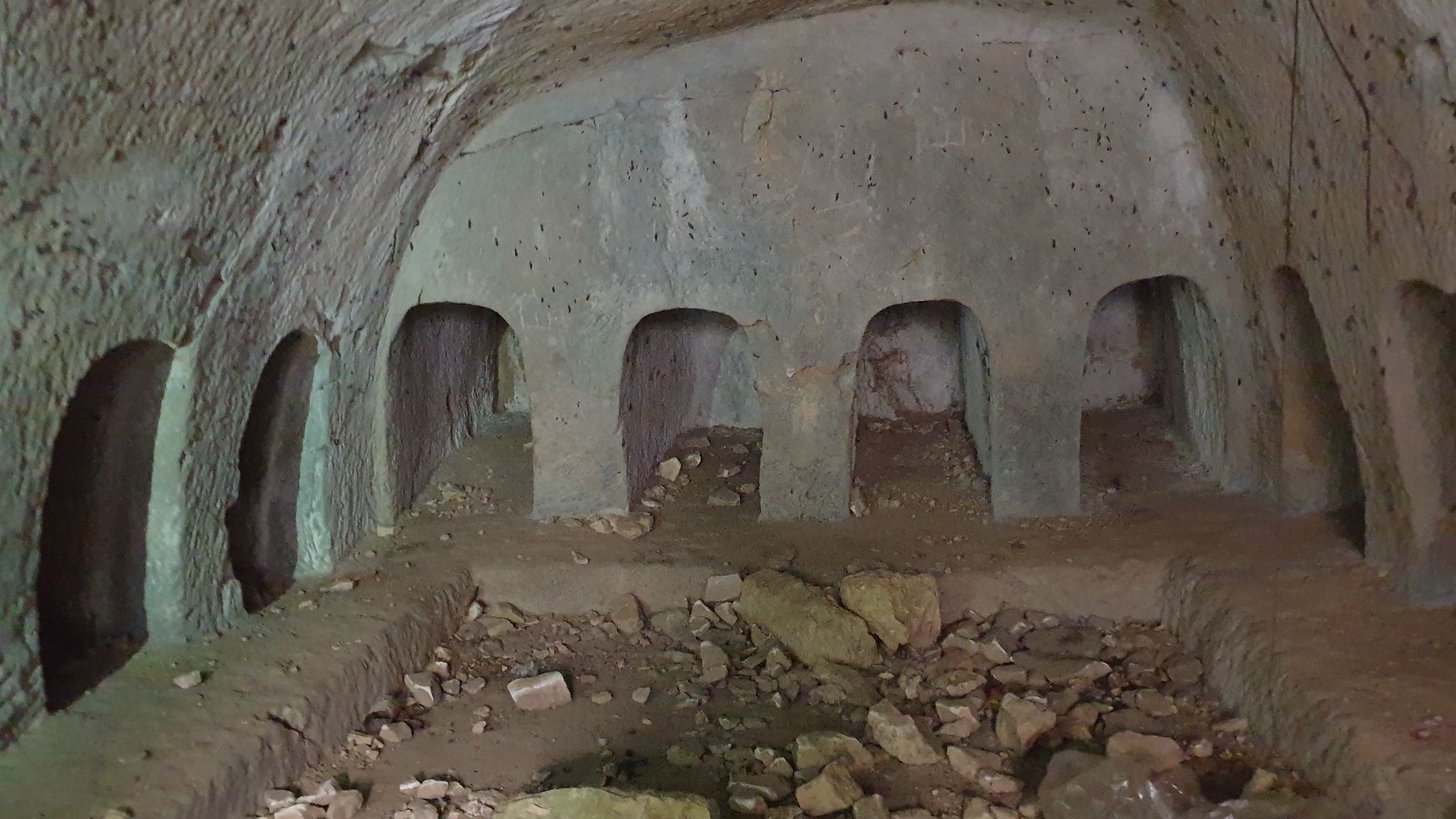
Inside The First-Century Burial Chamber
The tomb’s design begins with a modest vestibule and continues into a deeper chamber. It mirrors first-century Jewish burial architecture. The familiar arrangement supports the longstanding tradition attached to the site and offers a realistic sense of how mourners first approached and experienced the location.
 Owenglyndur, Wikimedia Commons
Owenglyndur, Wikimedia Commons
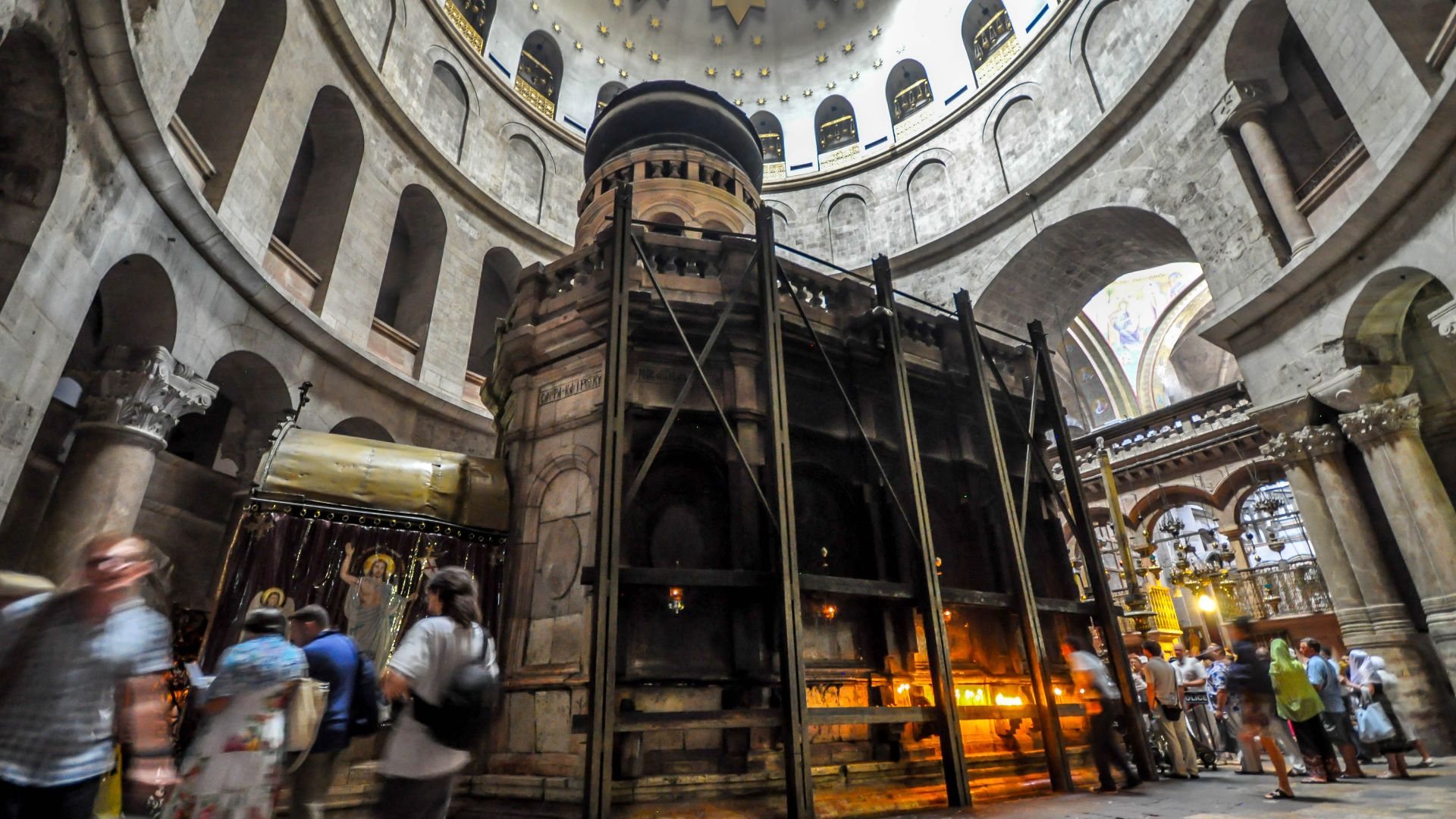
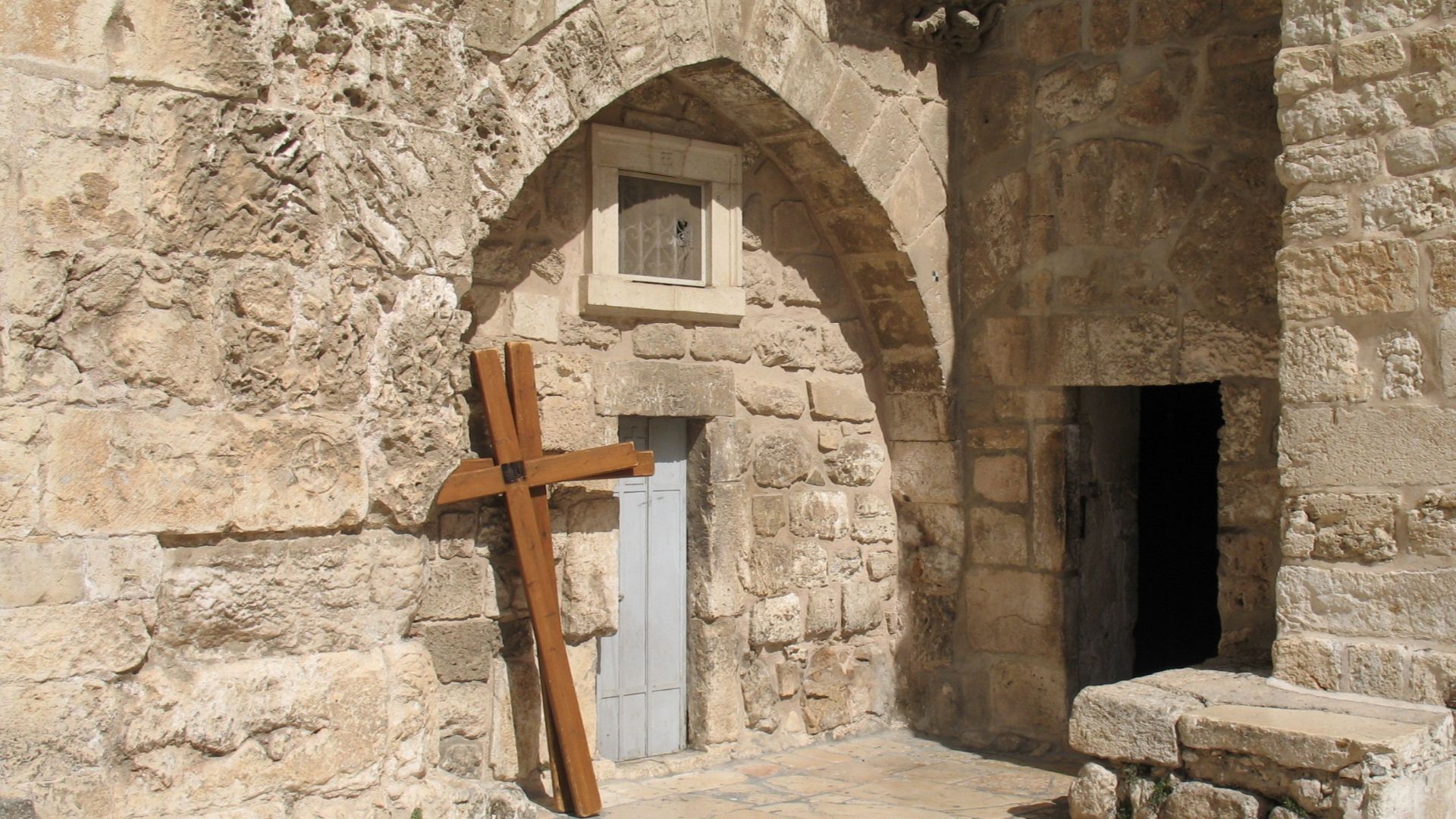
Why The Edicule Protects The Tomb Today
The Edicule, a small shrine housing the tomb, shelters the chamber from further deterioration. Its repeated rebuilding reflects efforts by various Christian communities to preserve sacred memory while stabilizing fragile stonework that has endured extensive environmental stress and historical violence over many centuries.
Centuries Of Damage And Reconstruction
The tomb has changed through earthquakes, fires, and reconstructions. The original chamber suffered damage over time, and later architects rebuilt protective structures around it. These transformations complicate archaeological analysis while illustrating persistent devotion across centuries of political and cultural upheaval.
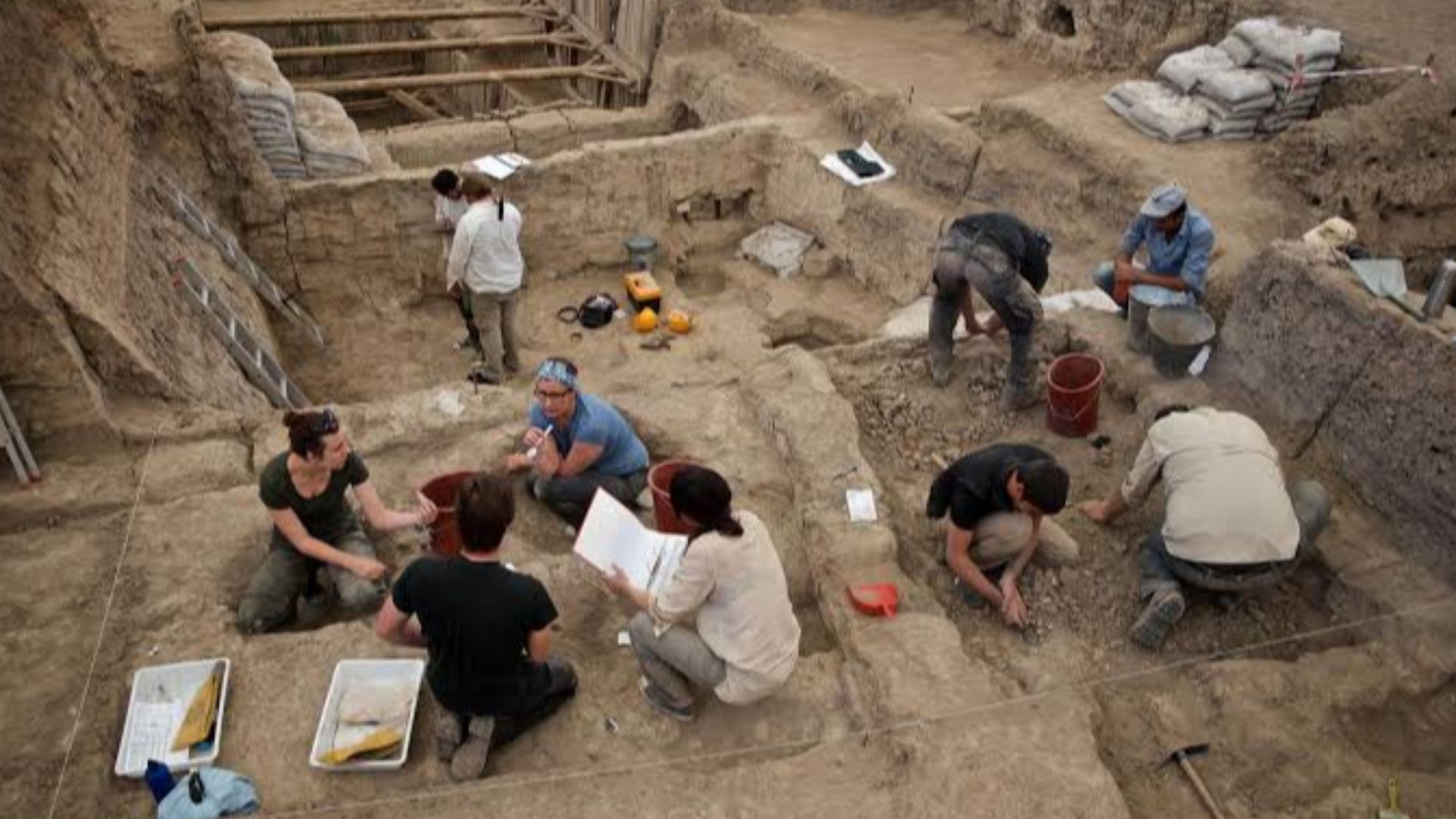
The Moment The Original Limestone Was Revealed
In 2016, the National Technical University of Athens team, led by Dr. Antonia Moropoulou, lifted the marble slab covering the chamber for the first time since 1555. They uncovered a Crusader-era marble layer and the original limestone burial bench beneath it.
 Thomas Bjørkan, Wikimedia Commons
Thomas Bjørkan, Wikimedia Commons
Restoring And Protecting The Tomb
During the restoration, specialists stabilized the Edicule, installed modern supports, and documented previously inaccessible areas. Their work revealed layers hidden for generations and provided invaluable information about the tomb’s earliest surviving features.
Lifting The Marble Slabs Layer By Layer
When restorers lifted the marble slab, they found an older marble layer and a limestone bench beneath it. This sequence of coverings showed how successive generations protected the burial surface and offered physical evidence of continuous reverence extending back many centuries.
 runkokokrun, Wikimedia Commons
runkokokrun, Wikimedia Commons
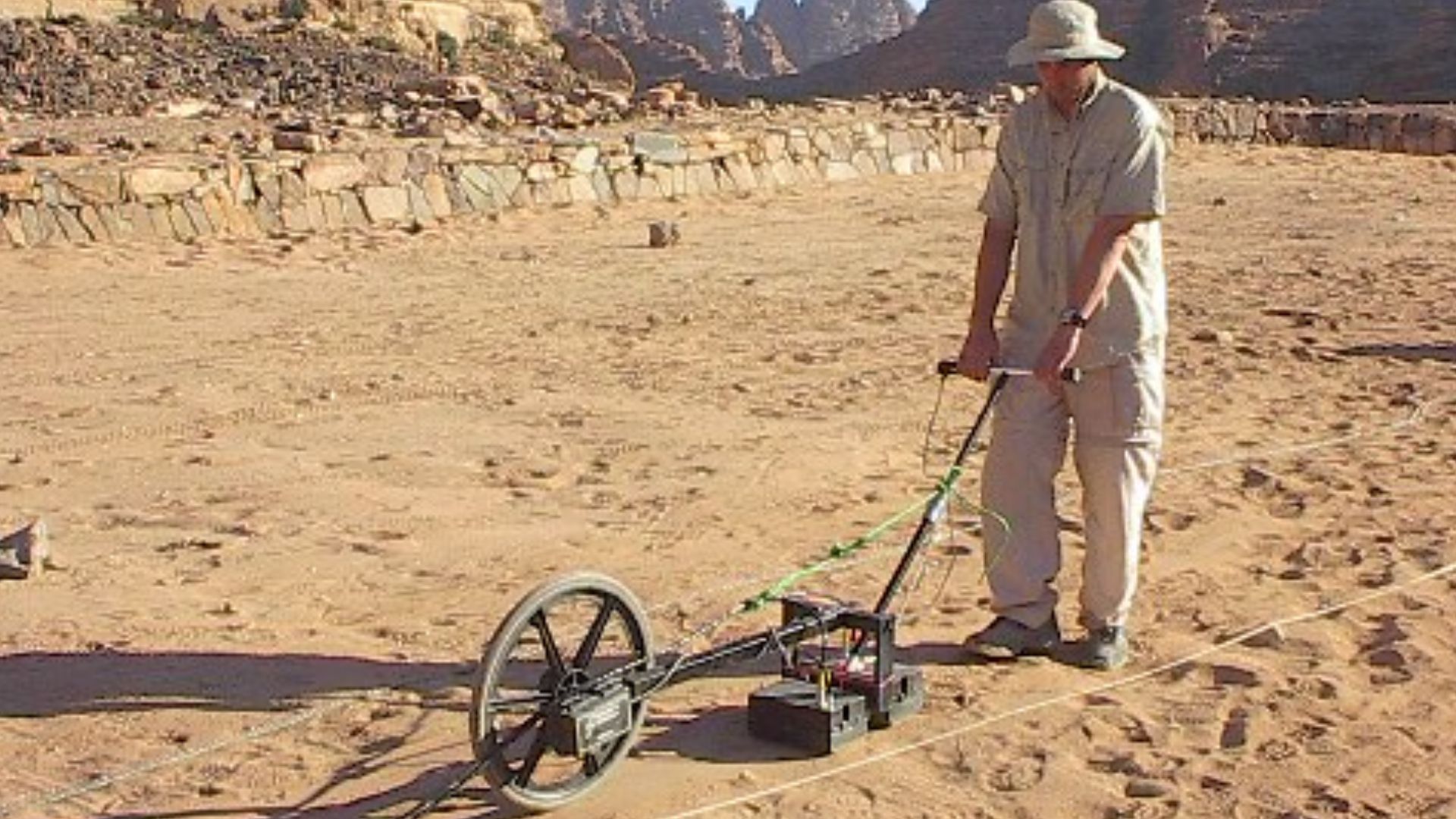
Science Tools That Mapped The Hidden Chamber
Researchers used ground-penetrating radar, thermography, and 3D mapping during the 2016 restoration, as documented by National Geographic and NTUA. These non-invasive tools revealed subsurface layers, which allowed experts to study construction phases, assess structural conditions, and visualize how early builders shaped the burial chamber.
 Archaeo-Physics LLC, Wikimedia Commons
Archaeo-Physics LLC, Wikimedia Commons
Why The Limestone Bench Matters So Much
The limestone bench aligns with descriptions of where Jesus’s body was laid. Its discovery beneath centuries of marble confirmed traditional expectations regarding the tomb’s original form. That encourages scholars to reassess earlier doubts about the site’s preservation and underlying archaeological reliability.
Pilgrims Who Have Come For Centuries
Findings like the limestone bench also echoed what generations of visitors experienced inside the chamber. Pilgrims have come since antiquity, and their written accounts shaped early liturgy and devotion. Despite shifting politics and borders, steady pilgrimage kept the tomb central to Christian spiritual geography.
 Henry Bacon, Wikimedia Commons
Henry Bacon, Wikimedia Commons
Why Millions Still Visit The Site
Millions travel to the tomb seeking a connection to Christianity’s foundational events. For many believers, standing near the burial chamber offers emotional closeness to Jesus’s final days. That reinforces faith through physical space rather than written tradition alone, especially within Jerusalem’s layered sacred area.
 Robert W. Weir (photograph courtesy Architect of the Capitol), Wikimedia Commons
Robert W. Weir (photograph courtesy Architect of the Capitol), Wikimedia Commons
Shared Custodianship Among Christian Traditions
Several Christian communities share custodianship of the tomb. The Status Quo agreement governs responsibilities among Greek Orthodox, Armenian Apostolic, and Roman Catholic authorities. Cooperation is sometimes challenging, yet shared reverence ensures the site remains accessible to worshippers from diverse traditions.
 Alfred Khazarian, Wikimedia Commons
Alfred Khazarian, Wikimedia Commons
How The Tomb Shaped Christian Geography
The tomb’s importance elevated Jerusalem as a major pilgrimage center. Routes, monasteries, and hospices developed to serve visitors, shaping the city’s layout. These networks highlight how a single sacred location influenced regional development and long-distance travel patterns across centuries of Christian history.
How Art Kept The Tomb’s Story Alive
Artists across centuries portrayed the tomb in icons, manuscripts, frescoes, and paintings. These images shaped collective imagination around the resurrection, influencing how Christians visualize the burial chamber. Art preserved continuity despite architectural changes, which kept the tomb’s narrative alive in global culture.
 Maerten de Vos, Wikimedia Commons
Maerten de Vos, Wikimedia Commons
What The Tomb Represents In Christian Theology
The tomb symbolizes Jesus’s real death and bodily resurrection. Its emptiness affirms Christian teachings about victory over death, which forms the basis of Easter celebrations. The physical site acts as a tangible expression of doctrines that shaped global Christian identity for two millennia.
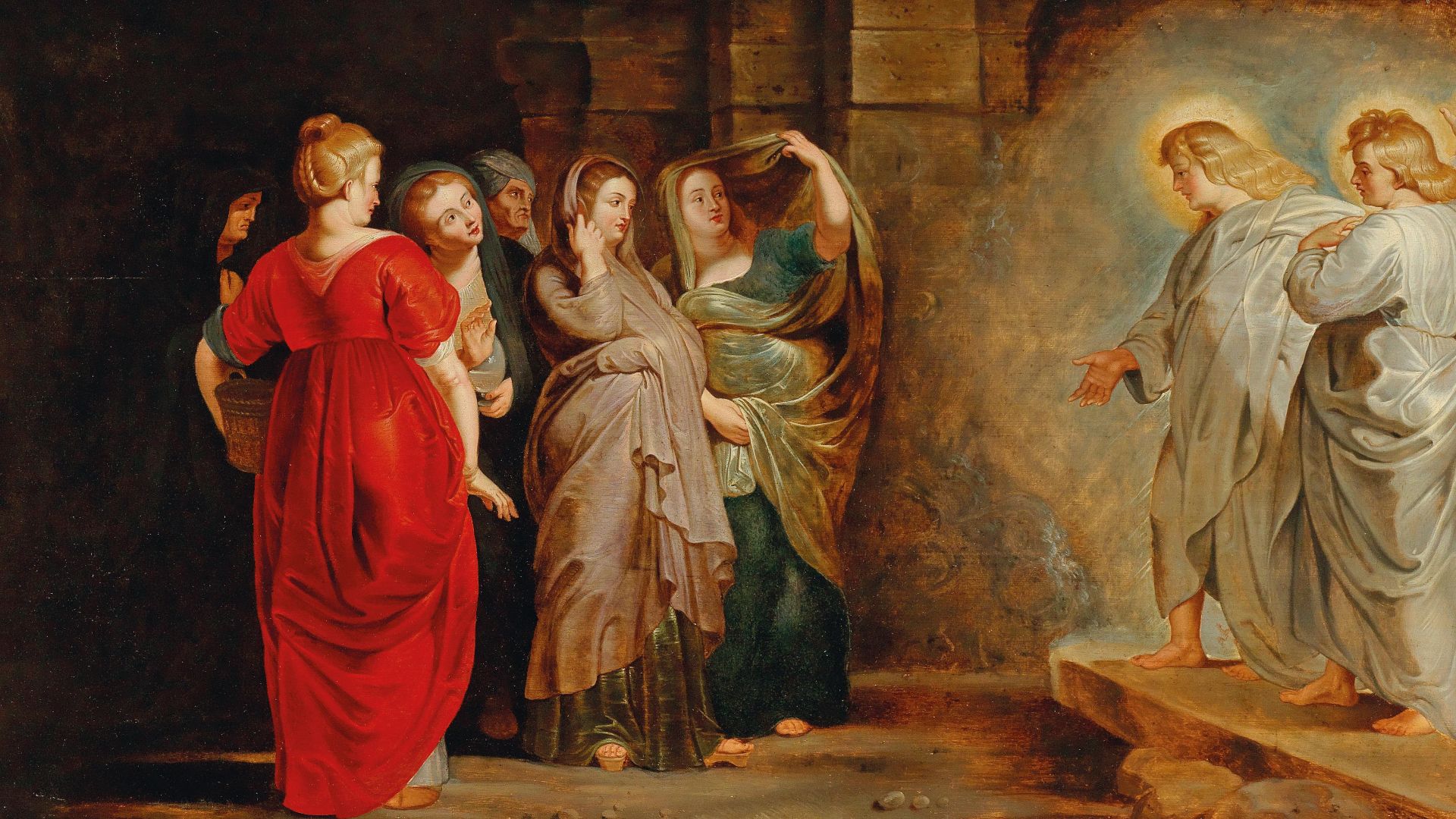 Workshop of Peter Paul Rubens, Wikimedia Commons
Workshop of Peter Paul Rubens, Wikimedia Commons
How The Tomb Influenced Christian Liturgy
Liturgical ceremonies surrounding Easter reference Jesus’s burial and rising from the tomb. Rituals such as Holy Saturday processions draw heavily from the site’s symbolism. They demonstrate how a physical location profoundly shaped spiritual practices within diverse Christian communities across many historical periods.
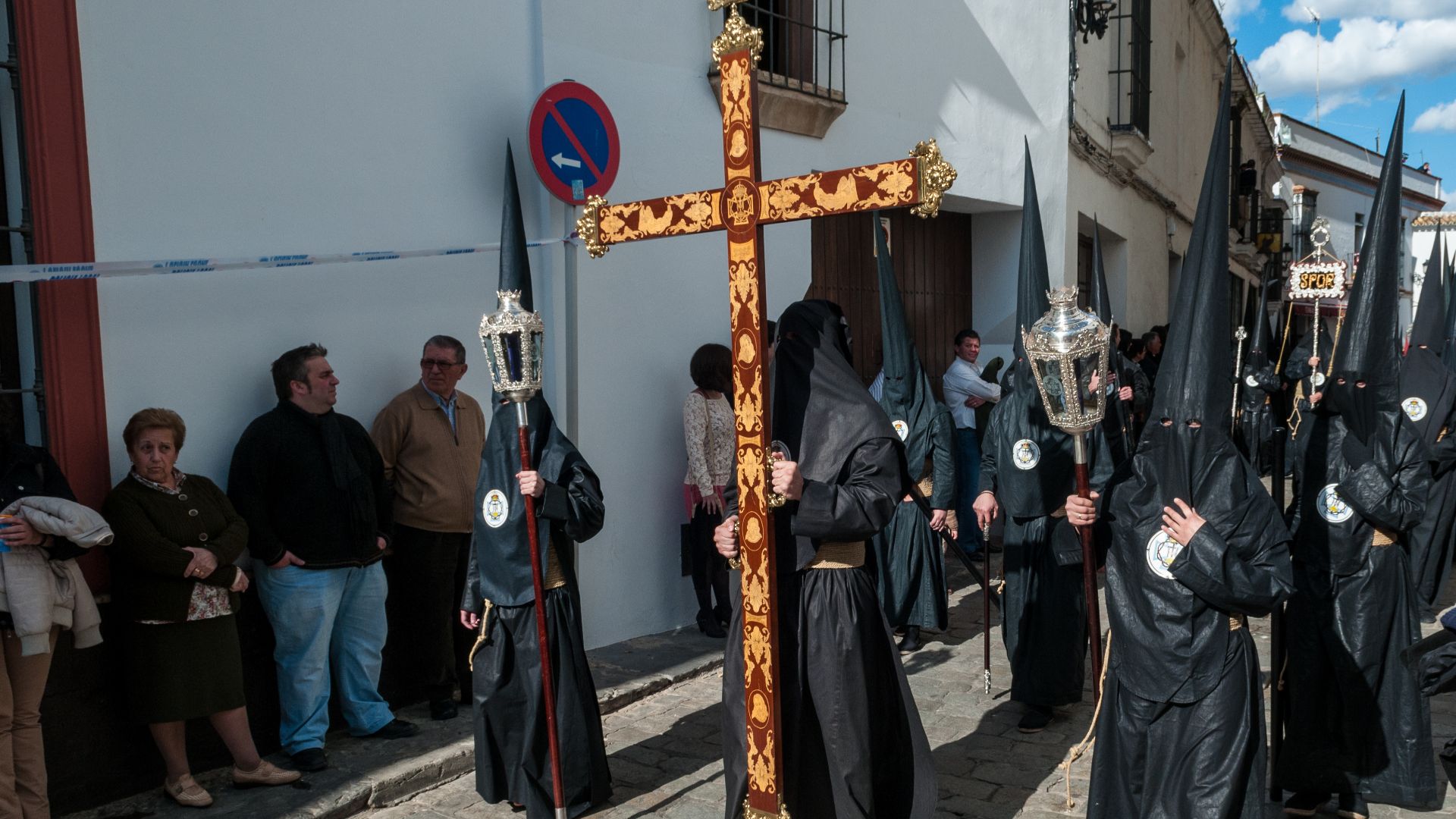 Michal Osmenda from Brussels, Belgium, Wikimedia Commons
Michal Osmenda from Brussels, Belgium, Wikimedia Commons
Where Faith And Archaeology Meet
The tomb’s influence on worship also highlights why researchers approach it from more than one angle. Archaeologist Shimon Gibson argues that archaeology and tradition must be weighed together. Scientific work provides context, while faith shapes meaning. They keep the site significant to scholars and believers alike.
What Scholars Debate About Authenticity
Historians debate how much of the current structure reflects the original burial site. Centuries of rebuilding obscure early features, creating uncertainty about precise details. Yet continuity of worship and ancient testimony maintain strong support for identifying the Holy Sepulchre as Jesus’s tomb.
 Dr._Colleen_Morgan from York, UK, Wikimedia Commons
Dr._Colleen_Morgan from York, UK, Wikimedia Commons
Why Absolute Proof Can Never Be Reached
Because Jerusalem contains thousands of ancient tombs, identifying one with absolute certainty is unrealistic. Plausibility is evaluated through alignment with texts, geography, and archaeological patterns. This framework explains why the Holy Sepulchre remains the strongest candidate despite historical gaps.
The Garden Tomb Is Appealing, But Too Ancient
Recognizing that certainty is impossible helps explain why some alternatives gained attention. The Garden Tomb’s quiet atmosphere once persuaded many nineteenth-century Protestants. Later archaeological work, especially by archaeologist Gabriel Barkay, dated its features to the Iron Age, showing it predates the first century. Therefore, it’s incompatible with the Gospel’s burial setting.
Talpiot Is A Tomb With Familiar Names
After the Garden Tomb proved too old, attention shifted to discoveries that seemed closer to the right period. The 1980 Talpiot excavation uncovered ossuaries bearing names that resembled those of Jesus’s family. Media excitement followed, but those names were widespread in the first century.
Why The Inscriptions Don’t Convince Scholars
One ossuary bore text some interpreted as “Jesus, son of Joseph.” The inscription is partially unclear, and paleographers disagree about its reading. Combined with statistical name frequency issues, the evidence remains insufficient to associate the Talpiot tomb with Jesus confidently.
A Tomb Too Wealthy For Jesus’s Background
As you look at the Talpiot tomb’s carved details and structured design, it reads as the product of substantial resources. That level of wealth contrasts sharply with Jesus’ Galilean origins, which is why scholars remain skeptical that this tomb matches early Christian burial traditions.
 Debbie Turner, Wikimedia Commons
Debbie Turner, Wikimedia Commons
A Folklore-Driven Claim
Skepticism toward ornate tombs like Talpiot also helps explain why far-flung claims occasionally surface. Roza Bal in Kashmir, India, attracted fringe theories suggesting Jesus survived crucifixion and traveled east. When the evidence is assessed, historians find no credible link between the shrine and first-century Judea.
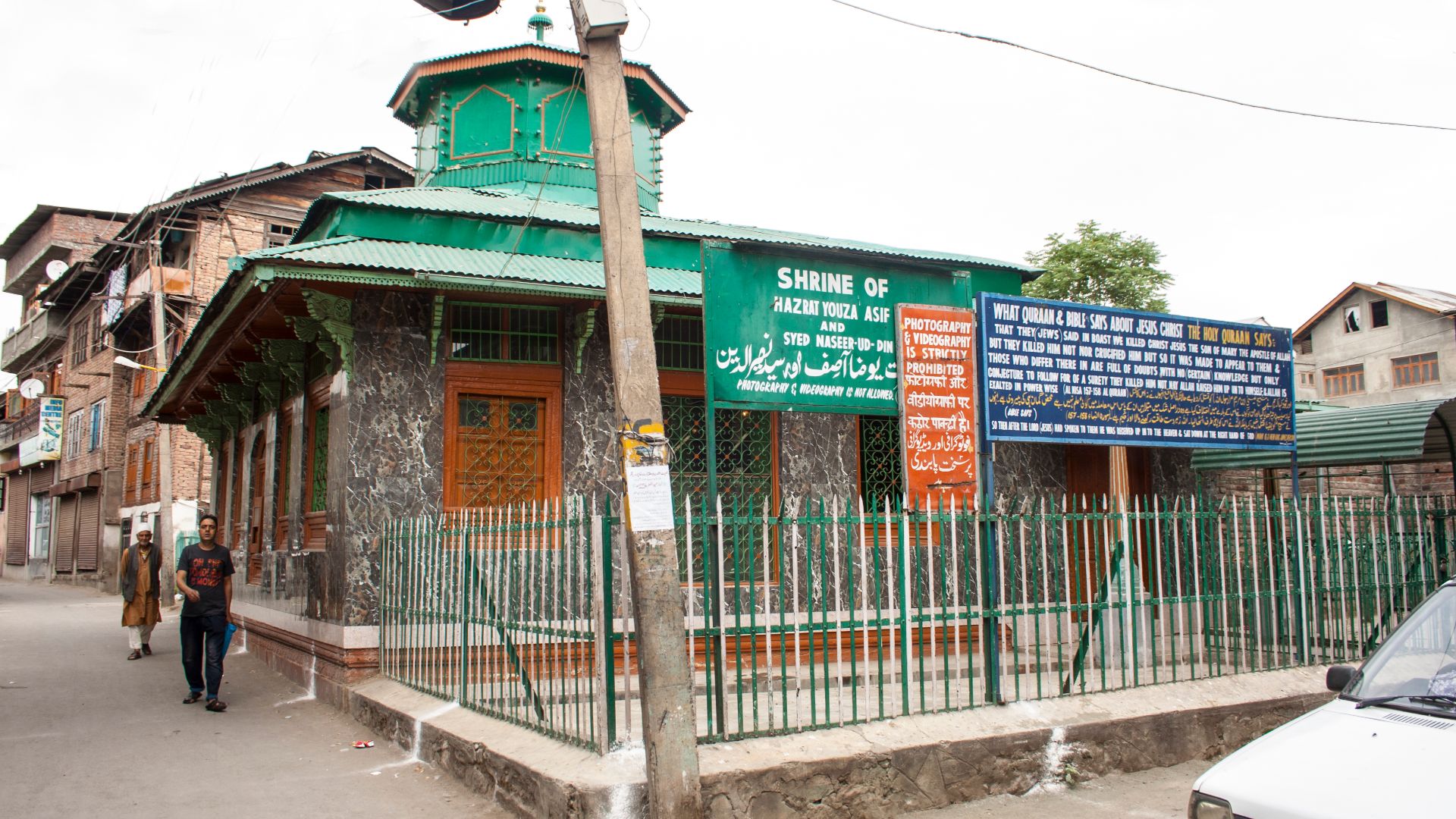 Indrajit Das, Wikimedia Commons
Indrajit Das, Wikimedia Commons
Japan’s ‘Jesus Lived Here’ Legend
The lack of evidence for Roza Bal mirrors another distant claim found in Japan’s Shingo village, where local lore insists Jesus escaped execution and settled there. The tale relies on invented genealogies and unverifiable travel stories. Historians dismiss it for the same reason.
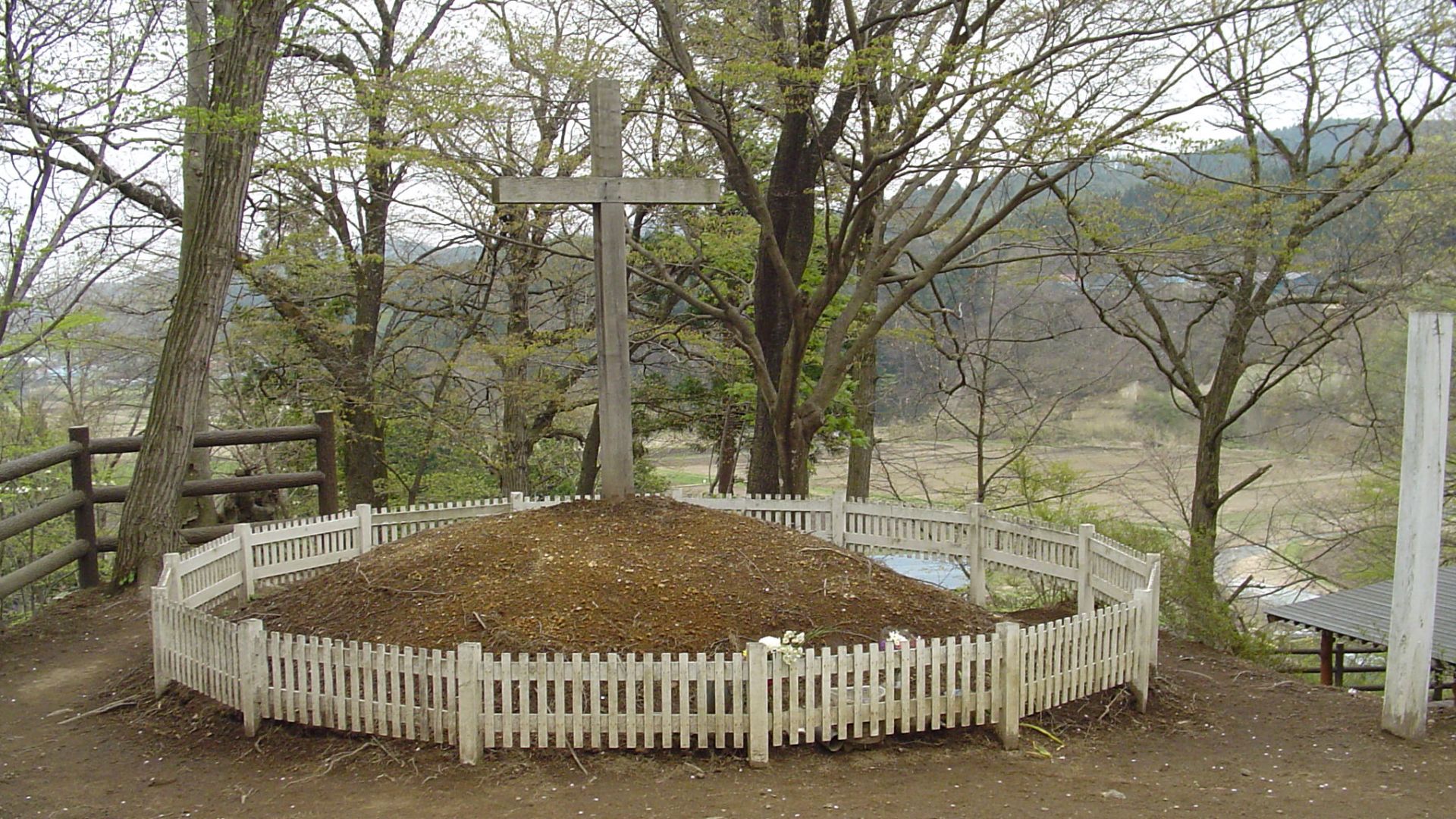 thor hestnes, Wikimedia Commons
thor hestnes, Wikimedia Commons
What Fringe Theories Reveal About Curiosity
You might notice that fringe theories, while unfounded, reveal an ongoing fascination with Jesus. Setting those ideas beside archaeological and historical evidence clarifies where genuine tradition stands. It also allows scholars to reaffirm the Holy Sepulchre’s enduring authority and separate credible memory from later imaginative narratives.
Continuity As A Form Of Evidence
Although fringe claims highlight curiosity, the long arc of Christian memory points in another direction. Continuous veneration at the Holy Sepulchre reaches back to antiquity, with early communities consistently identifying the site. Later construction preserved that focus to give the location a historical depth that competing proposals lack.
 Wayne McLean, user jgritz, Wikimedia Commons
Wayne McLean, user jgritz, Wikimedia Commons
Global Fascination With The Tomb
The tomb attracts scholars, pilgrims, filmmakers, and writers. Its layered history invites exploration of faith, memory, and identity. Every generation revisits the site’s meaning, illustrating how ancient spaces continue shaping modern cultural imagination far beyond their geographical boundaries.
 AiClassEland at English Wikibooks, Wikimedia Commons
AiClassEland at English Wikibooks, Wikimedia Commons
A Symbol That Reaches Beyond History
Even without definitive archaeological certainty, the tomb symbolizes hope and transformation. Its narrative invites reflection on mortality and renewal. And that’s how the site has enduring relevance for believers and nonbelievers seeking meaning in the story that shaped much of Western cultural development.