Inside Saturn’s Skies
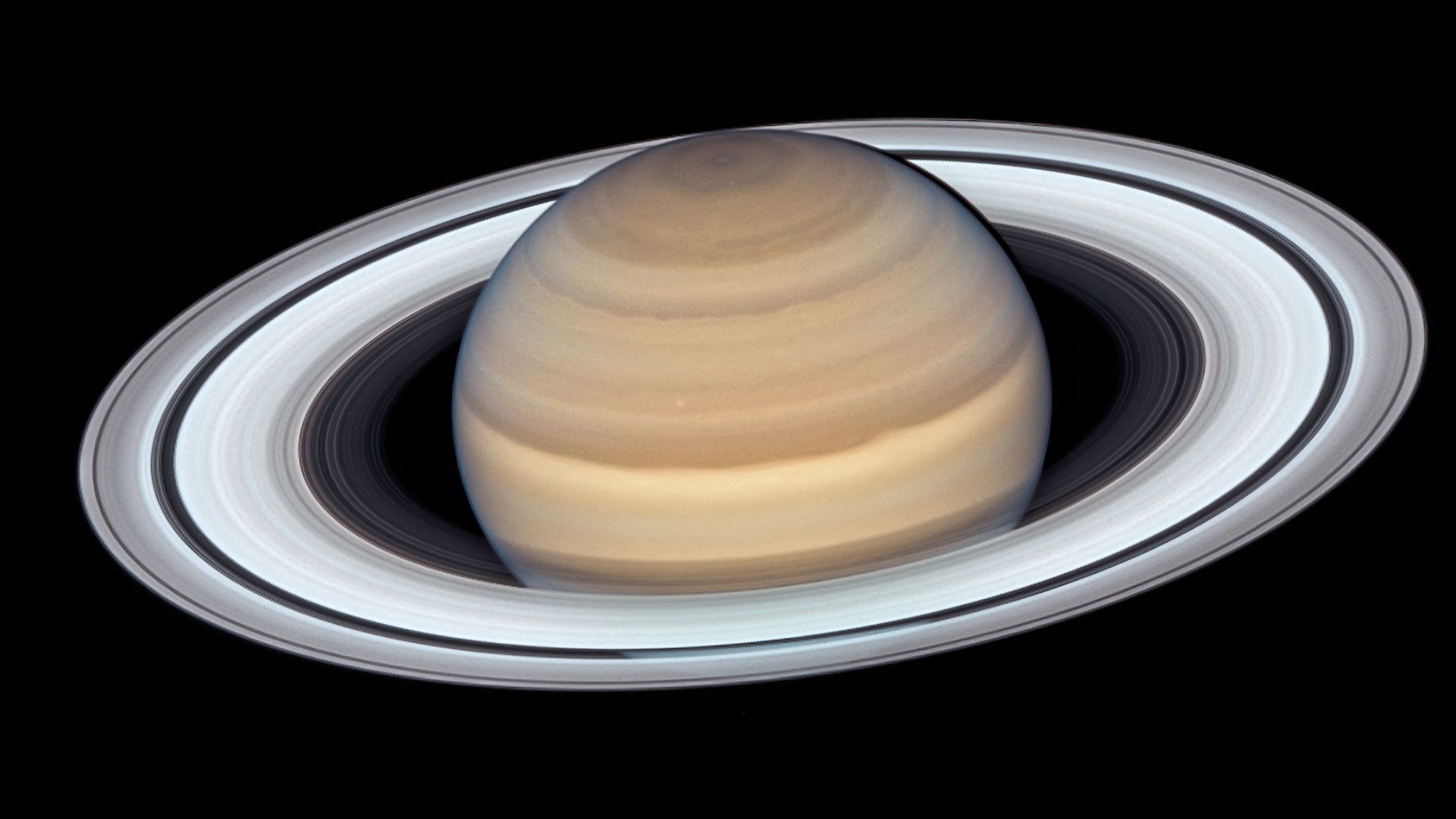
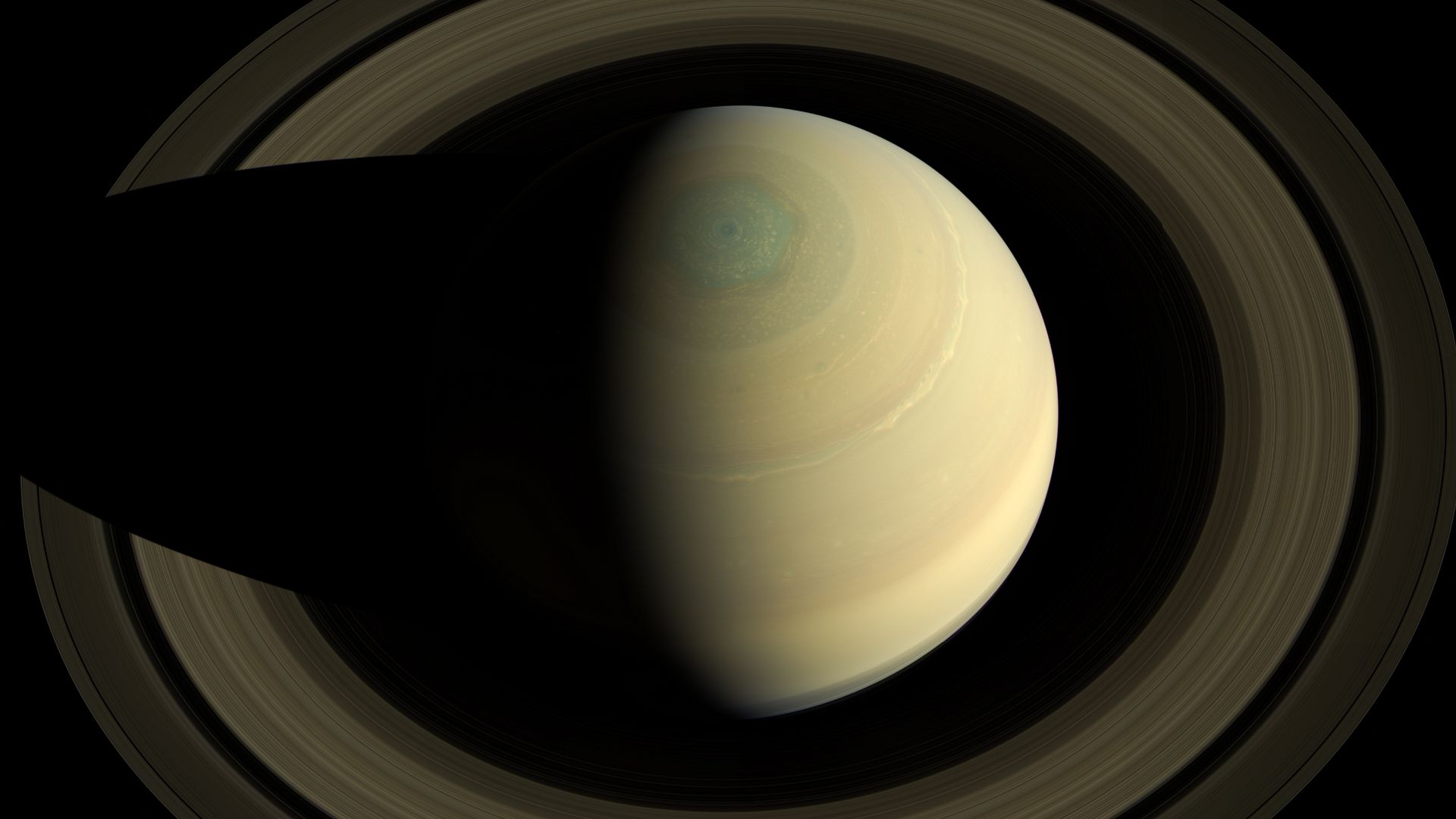
Saturn, the solar system’s elegant showpiece, has just revealed something astonishing. When the James Webb Space Telescope turned its gaze toward the ringed giant, it found geometry.

Rewriting The Rules
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) continues to exceed expectations by capturing phenomena that earlier missions could never detect. Designed primarily for deep-space observations, it’s now transforming planetary science. By using infrared vision, JWST can peer through dense atmospheres to show structures and chemical activity invisible to previous spacecraft and Earth-based telescopes.
 NASA Goddard Space Flight Center from Greenbelt, MD, USA, Wikimedia Commons
NASA Goddard Space Flight Center from Greenbelt, MD, USA, Wikimedia Commons
Why Saturn Still Holds Secrets Worth Chasing
Though visited by Voyager and Cassini, Saturn remains a puzzle box of atmospheric and magnetic mysteries. Beneath its swirling ammonia clouds lies a dynamic world where magnetism and chemistry interact in unpredictable ways. Each new observation challenges models of how gas giants work, especially in regions untouched by sunlight for years.
A Giant Cloaked In Mystery
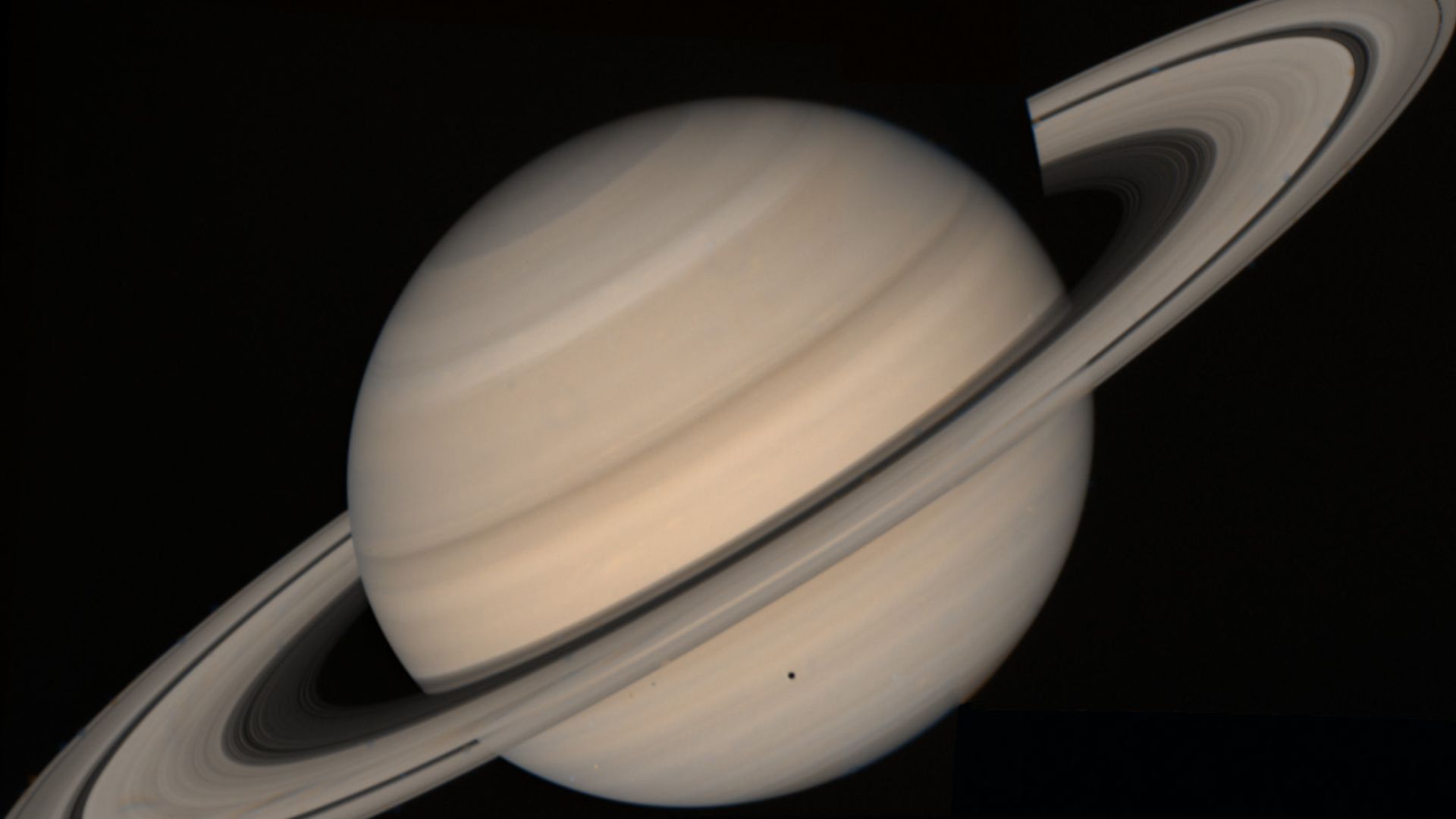
From Earth, Saturn’s creamy bands appear serene, but JWST’s instruments show a complex, layered atmosphere stretching thousands of miles deep. Hidden below its visible clouds are zones of turbulence, shifting temperatures, and chemical reactions driven by solar radiation and magnetic fields.
 NASA / JPL / Space Science Institute, Wikimedia Commons
NASA / JPL / Space Science Institute, Wikimedia Commons
The Night JWST Turned Its Gaze Toward The Ringed World
On November 29, 2024, JWST spent 10 continuous hours observing Saturn in the near-infrared spectrum. This marked its first long-duration planetary study. Scientists aimed to analyze faint emissions from hydrogen ions and methane to map upper-atmospheric behavior. What appeared in those images, however, defied every known expectation about Saturn’s skies.
 Bill Ingalls, Wikimedia Commons
Bill Ingalls, Wikimedia Commons
Ten Hours That Changed How We See Saturn
Across that ten-hour window, JWST’s spectrographs traced chemical fingerprints through multiple atmospheric layers. Researchers expected gentle gradients—broad, predictable bands of emission. Instead, they found intricate, small-scale patterns: dark spots, shifting arcs, and unexpected symmetry breaks. The data suggested Saturn’s upper atmosphere is far more dynamic and interconnected than scientists ever imagined.
 Bill Ingalls, Wikimedia Commons
Bill Ingalls, Wikimedia Commons
Peering Into The Planet’s Hidden Glow
Using its Near-Infrared Spectrograph, JWST detected faint emissions deep within Saturn’s upper atmosphere—light invisible to human eyes but rich in chemical information. These emissions revealed how molecules like hydrogen ions and methane react under extreme cold and magnetic influence, exposing hidden energy flows that maintain Saturn’s brilliant but deceptive glow.
 NASA/dima_zel, Wikimedia Commons
NASA/dima_zel, Wikimedia Commons
The Keys To Two Worlds Within One
Triatomic hydrogen, or H₃⁺, traces the ionosphere—an electrically charged layer energized by auroras—while methane dominates the denser stratosphere below. Studying both simultaneously lets scientists watch two vastly different systems interact. JWST’s precision revealed temperature shifts and structural contrasts that help explain how energy and chemistry connect Saturn’s upper and lower atmospheres.
What The Infrared Images Revealed Was Anything But Ordinary
When researchers converted infrared data into images, they saw something startling: Saturn’s emissions weren’t smooth or evenly distributed. Instead, intricate dark “beads” appeared like a chain across the ionosphere, and below them, a faint, star-like pattern emerged. These symmetrical yet incomplete shapes defied every established atmospheric model for gas giants.
 The New York Public Library, Unsplash
The New York Public Library, Unsplash

History's most fascinating stories and darkest secrets, delivered to your inbox daily.
Dark Beads Drifted Across Saturn’s Upper Sky
The so-called “dark beads” appeared as dim patches embedded within Saturn’s glowing auroral belt near the north pole. Unlike transient weather features, these persisted and drifted slowly. Scientists suspect interactions between Saturn’s fast rotation and magnetic field may sculpt these beads. However, their exact mechanism remains entirely unknown.
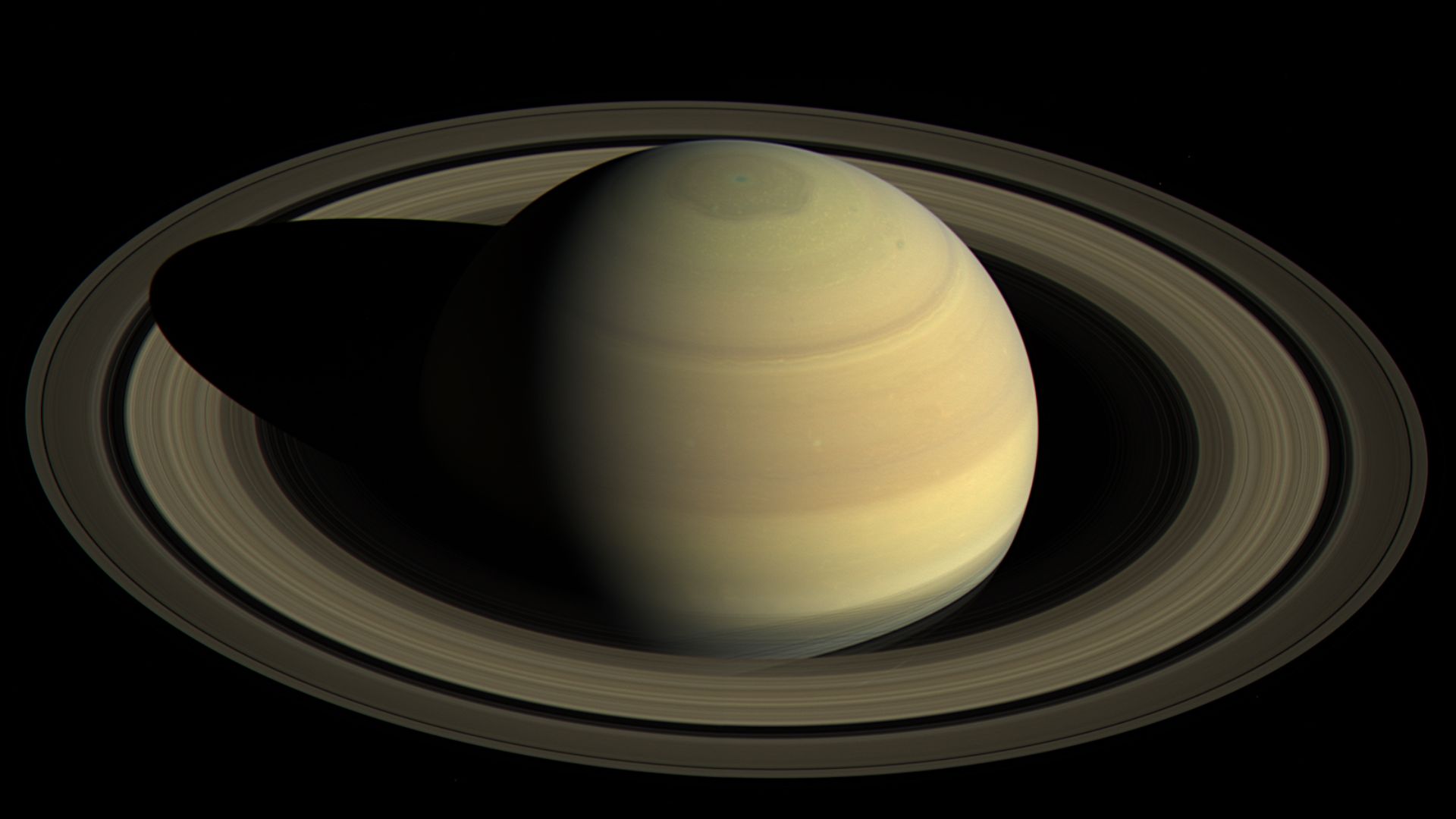 NASA/JPL-Caltech/SSI, Wikimedia Commons
NASA/JPL-Caltech/SSI, Wikimedia Commons
A Four-Armed Star Began To Take Shape
In Saturn’s stratosphere, JWST spotted a second anomaly—a star-shaped structure extending outward from the north pole. Only four of six expected arms appeared, forming an asymmetric pattern that stretched toward the equator. Its faint glow hinted at thermal and chemical shifts possibly linked to deeper storms or wave dynamics below.
 James Webb Space Telescope, Wikimedia Commons
James Webb Space Telescope, Wikimedia Commons
Scientists Expected Smooth Bands But Got Geometry Instead
Researchers anticipated broad, uniform emission zones shaped by Saturn’s rotation. Instead, JWST revealed precise, geometric forms—beads aligned like strings and a star pattern with missing arms. Such organized structures suggest forces beyond simple circulation, perhaps magnetic or gravitational, guiding energy and particles through Saturn’s vast and layered atmosphere.
 NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space Science Institute, Wikimedia Commons
NASA/JPL-Caltech/Space Science Institute, Wikimedia Commons
Patterns That Shouldn’t Exist Began To Align
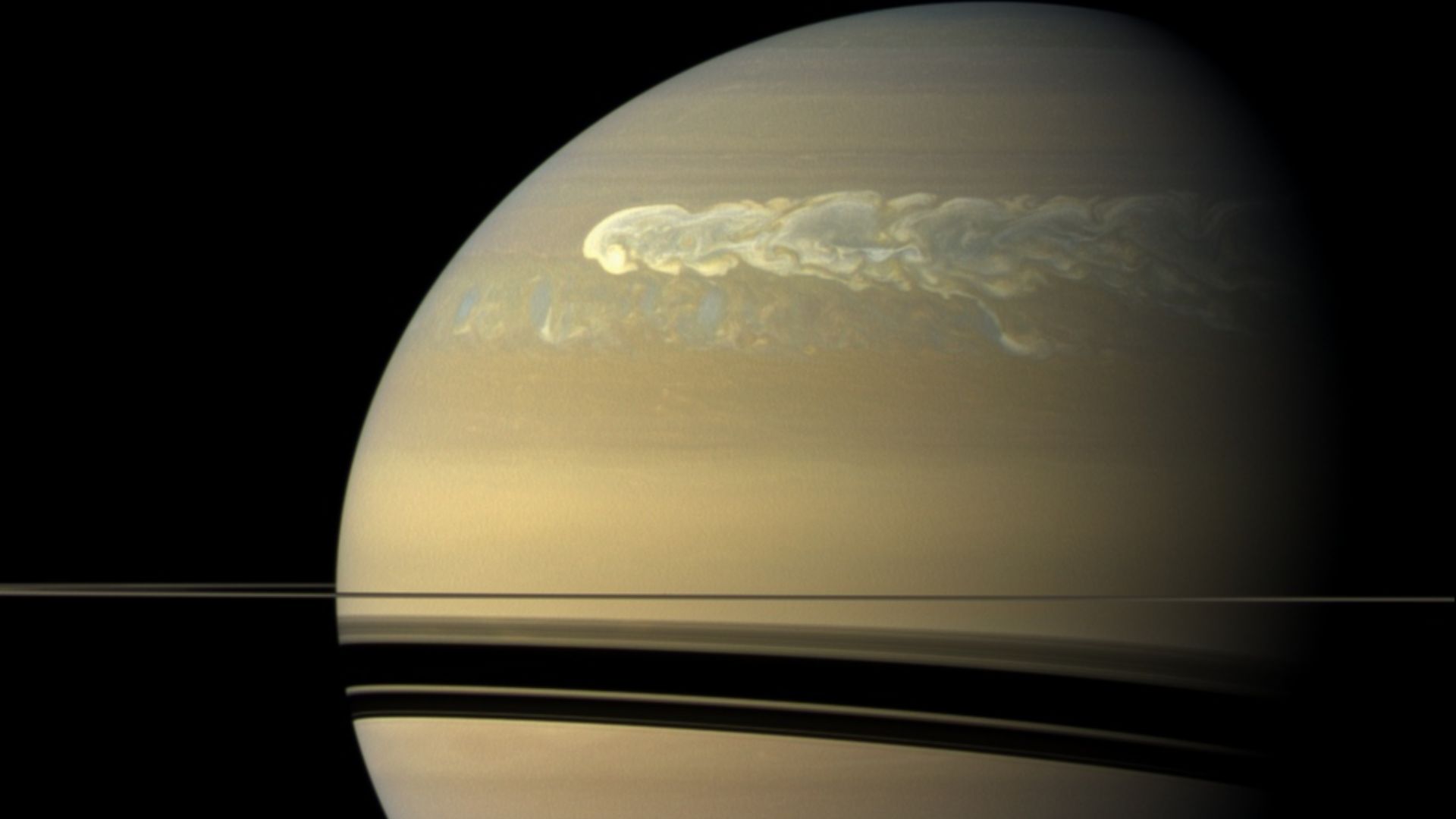
When scientists overlaid both layers—the ionosphere’s dark beads and the stratosphere’s star—they noticed alignments too specific to dismiss. The strongest “star arm” corresponded vertically to one of the darkest beads above. That correlation suggested a shared influence, possibly magnetic coupling, connecting regions separated by hundreds of vertical kilometers.
A Possible Conversation Between Layers Of Atmosphere
The apparent alignment hints that Saturn’s ionosphere and stratosphere might interact dynamically. Energy from auroras could ripple downward, while heat or wave motion could travel upward. This exchange challenges the long-held view that these layers act independently, instead suggesting vertical communication shaping Saturn’s weather and long-term atmospheric stability.
 NASA/JPL-Caltech/SSI, Wikimedia Commons
NASA/JPL-Caltech/SSI, Wikimedia Commons
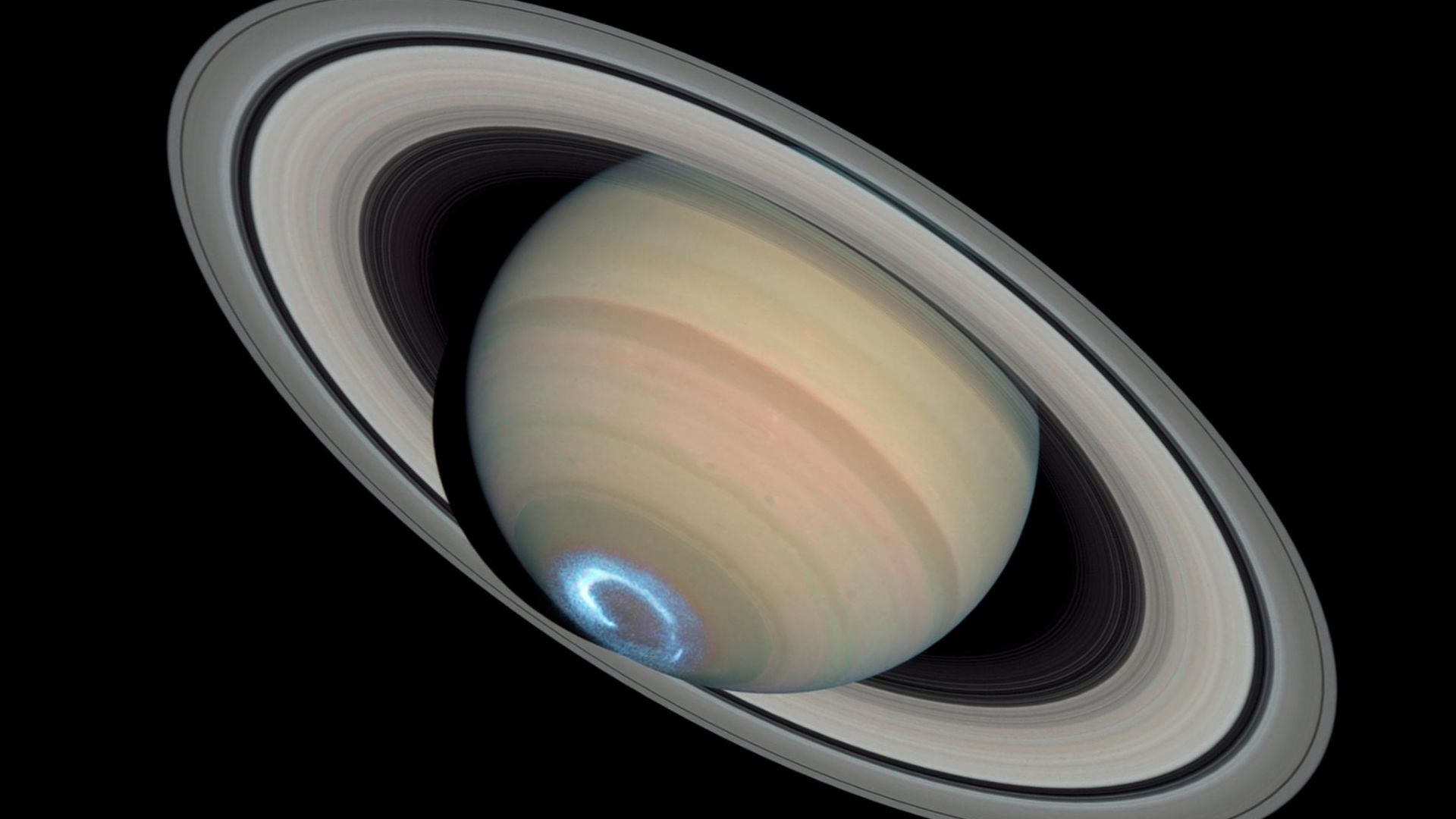
Magnetism Meets Motion
Saturn’s magnetic field rotates with its interior, sweeping charged particles through its atmosphere like an invisible turbine. These interactions generate auroras and heat high above the clouds. JWST’s findings imply that this magnetic power might also influence deeper airflows—creating patterns or even the mysterious bead-like formations scientists observed.
 NASA Hubble, Wikimedia Commons
NASA Hubble, Wikimedia Commons
Then Came The Question No One Could Answer
Could these strange shapes be a new form of auroral activity—or something entirely different? No previous mission, including Cassini’s 13-year Saturn survey, ever recorded such detail. The absence of precedent leaves scientists in a rare position: observing a phenomenon that defies current theories about planetary magnetism and weather.
 NASA/JPL-Caltech, Wikimedia Commons
NASA/JPL-Caltech, Wikimedia Commons
Could The Clues Lie In Saturn’s Famous Hexagon?
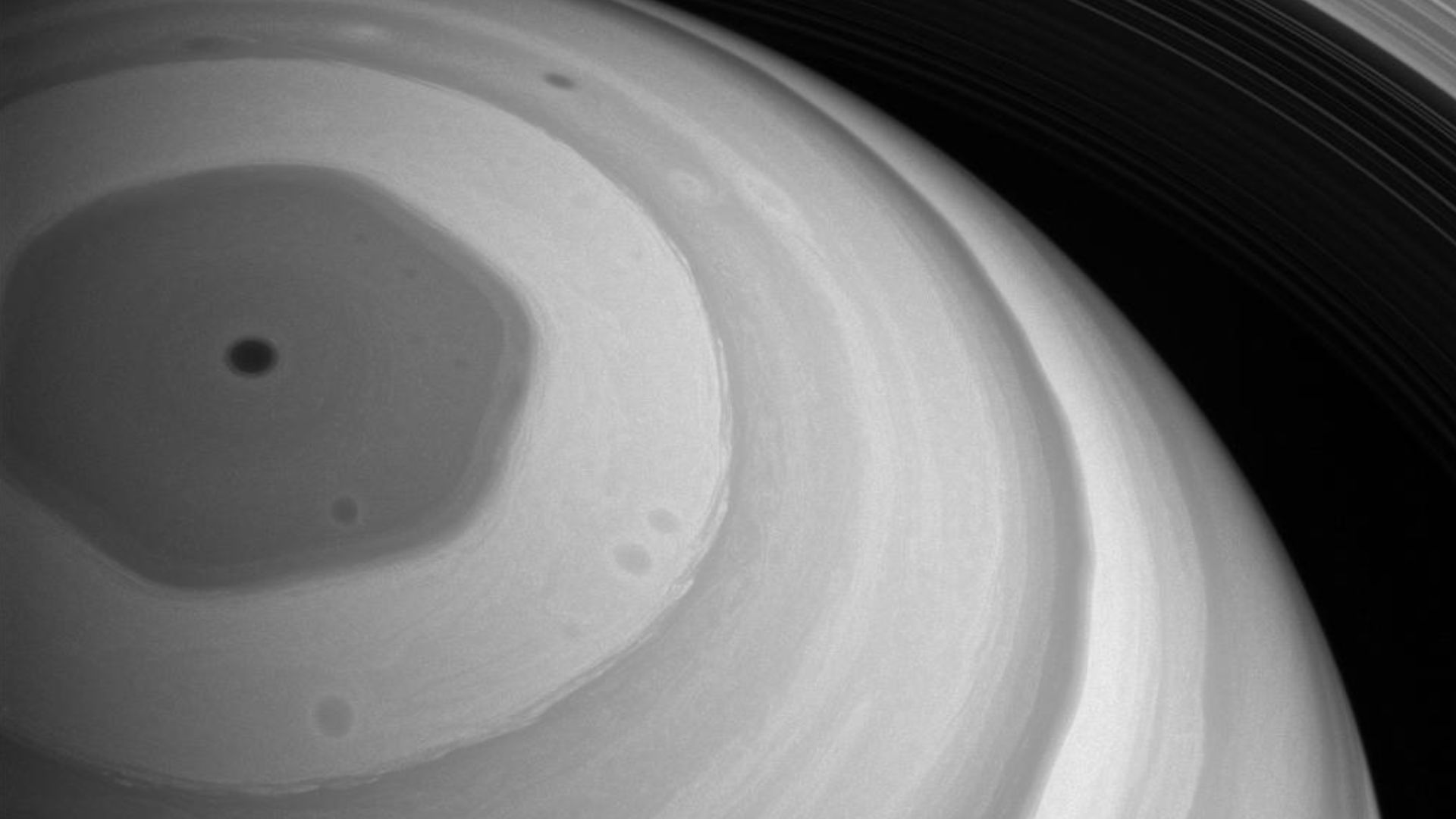
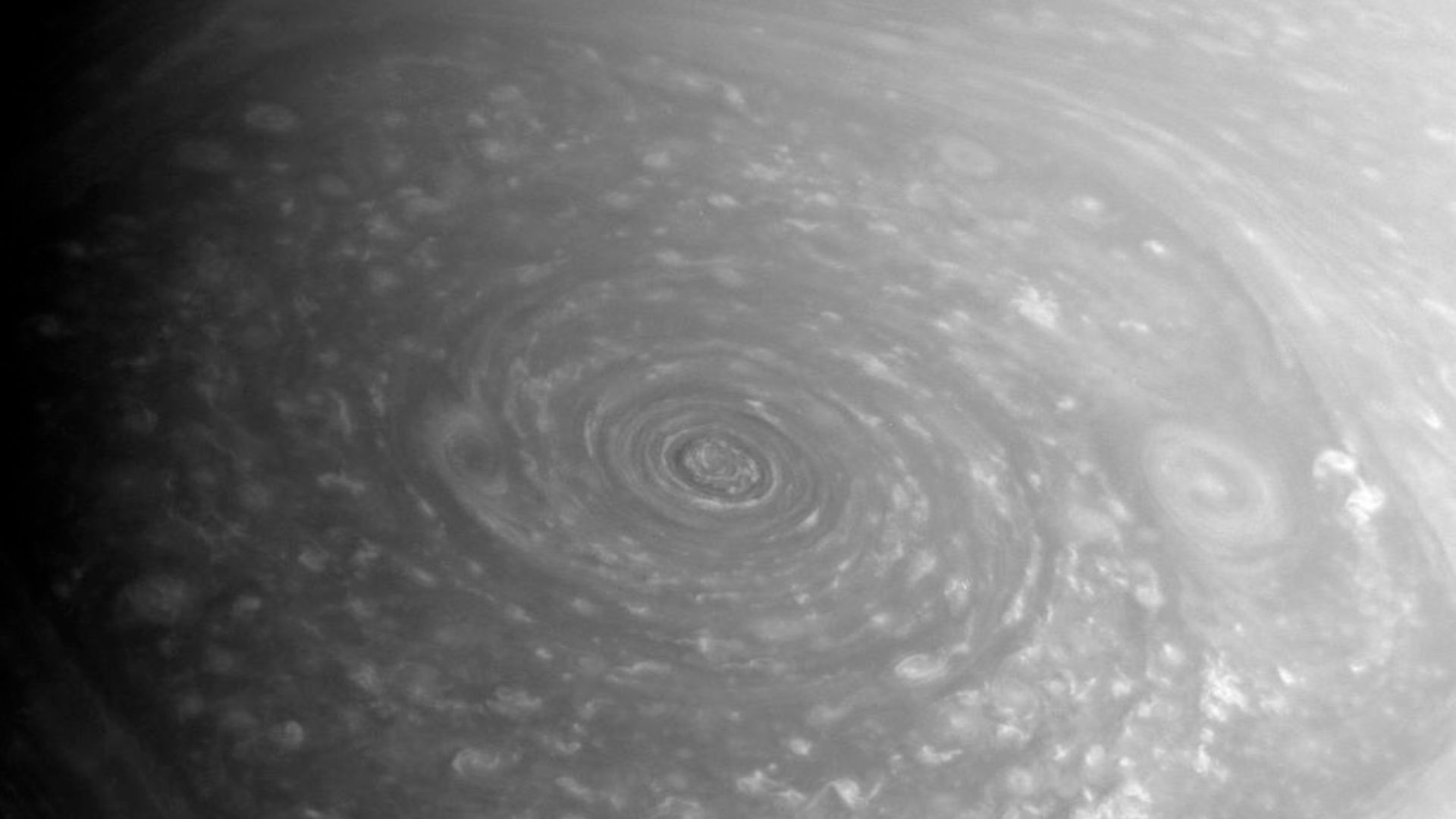
The discovery led scientists back to Saturn’s most enduring mystery—the hexagon storm encircling its north pole. This massive, six-sided jet stream spans about 20,000 miles across. JWST’s findings raised the question: could the star-shaped structure above be echoing that hexagonal pattern, linking deep atmospheric motion to higher energy layers?
 NASA / JPL-Caltech / Space Science Institute, Wikimedia Commons
NASA / JPL-Caltech / Space Science Institute, Wikimedia Commons
A Six-Sided Storm That Never Stops Spinning
Saturn’s hexagon is a standing wave in the atmosphere, persisting for decades. First seen by Voyager in the 1980s, it rotates in step with Saturn’s interior. Its stability suggests deep mechanical roots—possibly influencing, or being influenced by, the mysterious geometric shapes now seen above.
Is There A Hidden Connection?
When JWST’s maps were compared, something remarkable emerged: the star’s brightest arm extended directly above one hexagon side, while nearby beads aligned along similar longitudes. It’s uncertain whether this symmetry is a cause or a coincidence. Still, it hints that Saturn’s deep dynamics could resonate through multiple atmospheric layers like connected instruments.
 Bill Ingalls, Wikimedia Commons
Bill Ingalls, Wikimedia Commons
JWST Saw What Cassini Never Could
Cassini’s orbit provided close-up views of Saturn’s rings and clouds, but its instruments couldn’t detect the faint infrared emissions from high altitudes. JWST’s vantage point—one million miles from Earth—offers unmatched stability and sensitivity. That combination finally exposed delicate temperature and emission structures invisible even to Cassini’s advanced sensors.
Infrared Vision That Pierces Saturn’s Veil
Infrared light passes through thick layers that scatter visible wavelengths. JWST’s detectors measure this faint radiation, revealing composition and temperature deep within Saturn’s atmosphere. These capabilities turned what was once a hazy giant into a detailed energy map, exposing how its upper layers behave under magnetic and solar influence.
Astonishment In The Data Room
When the first images were processed, silence filled the research lab. The geometric formations were undeniable—patterns no algorithm could invent. Astronomers compared timestamps, checked calibration, and confirmed authenticity. It wasn’t noise or artifact; Saturn itself was speaking in shapes, and humanity had just learned a new dialect of its atmosphere.
 Bill Ingalls, Wikimedia Commons
Bill Ingalls, Wikimedia Commons
Tom Stallard’s Team Faces The Unexplainable
Led by Professor Tom Stallard of Northumbria University, the international team struggled to interpret what they saw. Stallard described the results as “completely unexpected”. His group, seasoned by years of planetary spectroscopy, realized that JWST had captured a phenomenon unseen in any other world and a true first in planetary science.
A Mystery That’s Reshaping Everything
The findings challenge how scientists understand energy movement on gas giants. Traditional models separate atmospheric layers into independent systems, but JWST suggests vertical coupling with energy, heat, and magnetism interacting across immense distances. Understanding this process could refine climate models not only for Saturn but for Jupiter and even exoplanetary atmospheres.
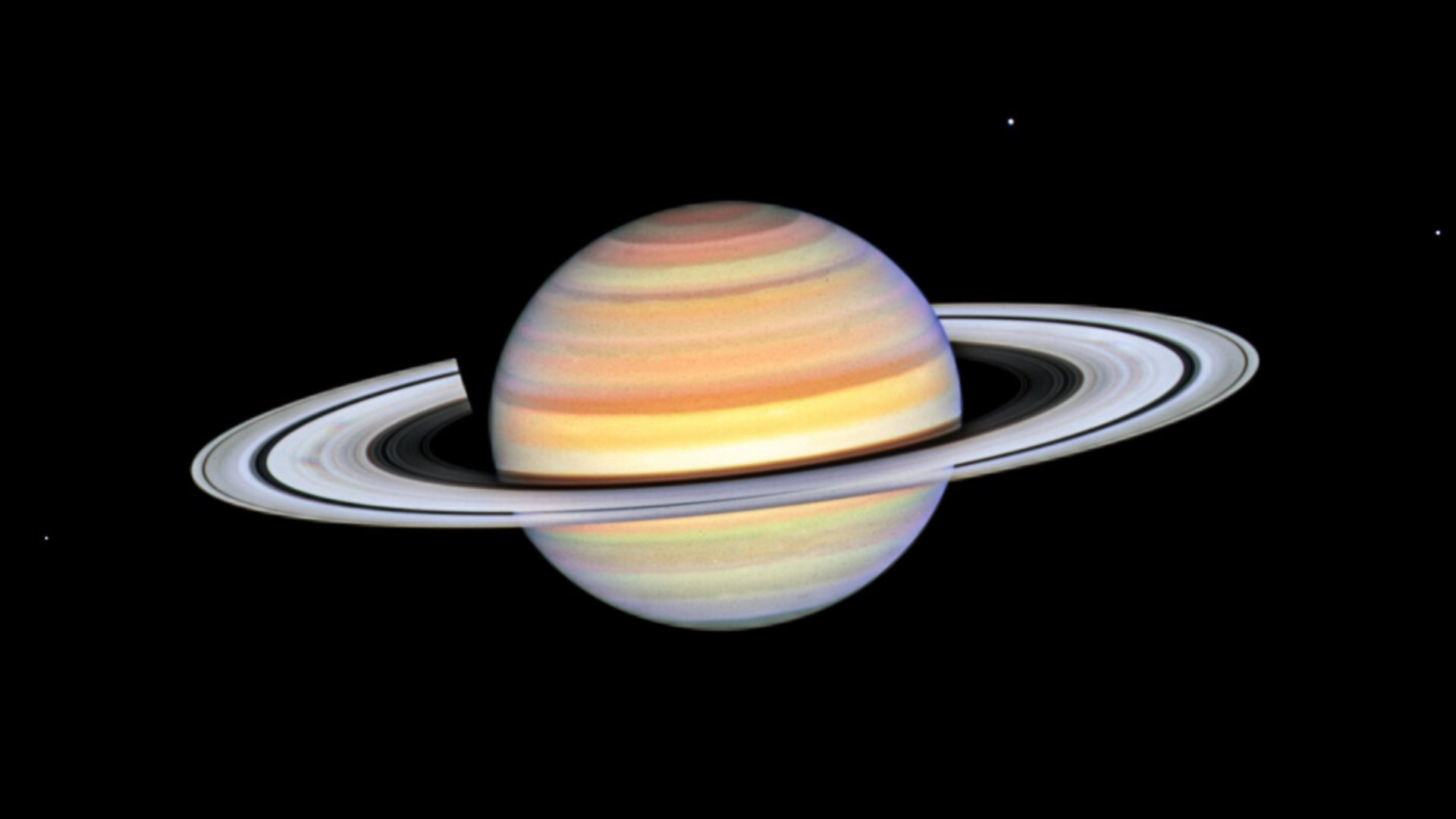 NASA, ESA, STScI, A. Simon (NASA-GSFC), Wikimedia Commons
NASA, ESA, STScI, A. Simon (NASA-GSFC), Wikimedia Commons
More Questions Than Answers, And That’s The Point
No definitive explanation yet connects the beads, the star, and the hexagon. Each observation opens new possibilities—from magnetospheric resonance to deep atmospheric waves. For scientists, unanswered questions aren’t failures but invitations. The unknown patterns above Saturn mark the beginning of a new chapter in comparative planetary research.
 NASA/JPL-Caltech/SSI/Cornell, Wikimedia Commons
NASA/JPL-Caltech/SSI/Cornell, Wikimedia Commons
The Universe Still Has Secrets
In the end, JWST’s discovery is less about solving Saturn’s puzzle than acknowledging its depth. Every new image proves how little we truly know about the worlds we’ve studied for decades. Saturn’s mysterious geometry stands as both a scientific enigma and a humbling reminder of the cosmos’ endless imagination.
 NASA's James Webb Space Telescope from Greenbelt, MD, USA, Wikimedia Commons
NASA's James Webb Space Telescope from Greenbelt, MD, USA, Wikimedia Commons